Abstract
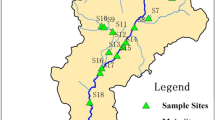
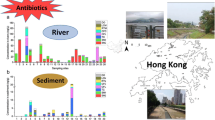
We evaluated the occurrence and distribution of 12 antibiotics from the sulfonamide (SAs), fluoroquinolone (FQs) and tetracycline (TCs) groups in the Weihe River, North China. The total antibiotic concentrations in surface water, pore water, and sediment samples ranged from 11.1 to 173.1 ng/L, 5.8 to 103.9 ng/L, and 9.5 to 153.4 μg/kg, respectively. The values of the sediment-water partitioning coefficient in the Weihe River varied widely, from not detected to 943, 2213, and 2405 L/kg for SAs, FQs, and TCs, respectively. The values of the partitioning coefficients between sediment and surface water were generally lower than those between sediment and pore water, which indicated ongoing inputs to the water. The risk assessment showed that there were relatively high ecological risks to aquatic algae in this area from sulfamethoxazole, norfloxacin, tetracycline, ofloxacin, and ciprofloxacin.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrieu M, Rico A, Minh Phu T, Thanh Huong DT, Phuong NT, Van den Brink P (2015) Ecological risk assessment of the antibiotic enrofloxacin applied to Pangasius catfish farms in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Chemosphere 119:407–414
Carballa M, Guido F, Omil F, Lema JM, Terns TA (2008) Determination of the solid water distribution coefficient (Kd) for pharmaceuticals, estrogens and musk fragrances in digested sludge. Water Res 42:287–295
Cheng WX, Lia JN, Wu Y, Xua LK, Su C, Qian, YY, Zhu YG, Chen H (2016) Behavior of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes ineco-agricultural system: a case study. J Hazard Mater 304:18–25
de Souza SM, Vasconcelos EC, Dziedzic M, de Oliveira CM (2009) Environmental risk assessment of antibiotics: an intensive care unit analysis. Chemosphere 77:962–967
EC (European Commission) (2003) European Commission Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93//67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances and Commission Regulation (EC) No.1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substance, Part II. In: Commission, E.,100–103
Gibs J, Heckathorn HA, Meyer MT, Klapinski FR, Alebus M, Lippincott RL (2013) Occurrence and partitioning of antibiotic compounds found in the water column and bottom sediments from a stream receiving two wastewater treatment plant effluents in Northern New Jersey, 2008. Sci Total Environ 458–460:107–116
Gong WW, Liu XH, He H, Wang L, Dai GH (2012) Quantitatively modeling soil–water distribution coefficients of three antibiotics using soil physicochemical properties. Chemosphere 89(7):825–831
Hu XG, He KX, Zhou QX (2012) Occurrence, accumulation, attenuation and priority of typical antibiotics in sediments based on long-term field and modeling studies. J Hazard Mater 226:91–98
Huang Y, Cheng M, Li W, Wu L, Chen Y, Luo Y, Christie P, Zhang H (2013) Simultaneous extraction of four classes of antibiotics in soil, manure and sewage sludge and analysis by liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry with the isotope-labelled internal standard method. Analy Methods 5:3721–3731
Kim SC, Carlson K (2007) Temporal and spatial trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in aqueous and river sediment matrices. Environ Sci Technol 41:50–57
Kümmerer K (2007) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—a review part-II. Chemosphere 75:435–441
LaPara TM, Burch TR, McNamara PJ, Tan DT, Yan M, Eichmiller JJ (2011) Tertiary-treated municipal wastewater is a significant point source of antibiotic resistance genes into Duluth-Superior Harbor. Environ Sci Technol 45:9543–9549
Lindberg RH, Fick J, Tysklind M (2010) Screening of antimycotics in Swedish sewage treatment plants-waters and sludge. Water Res 44:649–657
Managaki S, Murata A, Takada H, Tuyen BC, Chiem NH (2007) Distribution of macrolides, sulfonamides, and trimethoprim in tropical waters: ubiquitous occurrence of veterinary antibiotics in the Mekong Delta. Environ Sci Technol 41:8004–8010
Pruden A, Arabi M, Storteboom HN (2012) Correlation between upstream human activities and riverine antibiotic resistance genes. Environ Sci Technol 46:11541–11549
Rico A, Oliveira R, McDonough S, Matser A, Khatikarn J, Satapornvani K, K, Nogueira JA, Soares AMVM, Domingues I, Van den Brink PJ (2014) Use, fate and ecological risks of antibiotics applied in tilapia cage farming in Thailand. Environ Pollut 191:8–16
Sukul P, Lamshȍft M, Zühlke S, Spiteller M (2008) Sorption and desorption of sulfadiazine in soil and soil-manure systems. Chemosphere 73:1344–1350
Tang J, Shi TZ, Wu XW, Cao HQ, Li XD, Hua RM, Tang F, Yue YD (2015) The occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in Lake Chaohu, China: Seasonal variation, potential source and risk assessment. Chemosphere 122:154–161
Xu XR, Li XY (2010) Sorption and desorption of antibiotic tetracycline on marine sediments. Chemosphere 78:430–436
Xu WH, Zhang G, Zou SC, Li XD, Liu YC (2007) Determination of selected antibiotics in the Victoria Harbour and the Pearl River, South China using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Environ Pollut 145:672–679
Zhang T, Li B (2011) Occurrence, transformation, and fate of antibiotics in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 41:951–998
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (Project No. 41101473) and Funding scheme for the young backbone teachers of higher education institutions in Henan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Gao, J., Zhang, Q. et al. Distribution and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in a Typical River in North China Plain. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98, 478–483 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-2023-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-2023-0