Abstract
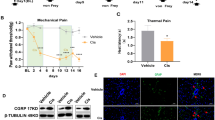
Neuroinflammatory response in spinal dorsal horn has been demonstrated to be a critical factor in oxaliplatin-induced pain. Melatonin has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and anti-allodynia effects in both preclinical and clinical studies. In the present study, we investigated the role of systemic administration of melatonin on oxaliplatin-induced pain. Intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection with oxaliplatin induced significantly mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. Melatonin (i.p.) significantly alleviated mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in the oxaliplatin but not sham-treated rats. The attenuation of nociceptive response persisted at least to 3 days after melatonin injection, throughout the entire observing window. Immunohistochemistry showed that oxaliplatin induced a significant increase of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunodensities, which could be suppressed by melatonin. Western blotting showed that GFAP protein levels were significantly elevated in the oxaliplatin-vehicle group. Melatonin significantly decreased oxaliplatin-induced upregulation of GFAP expressions. Oxaliplatin injection also enhanced the messenger RNA (mRNA) expressions of cytokines including interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and chemokines including monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and monocyte inflammatory protein-1 (MIP-1α) in the spinal dorsal horn, which could be significantly repressed by melatonin. In vitro study showed that mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, MCP-1, and MIP-1α in primarily astrocytes were significantly increased after lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1 μg/ml) stimulation. Melatonin (10 and 100 μM) greatly inhibited synthesis of these inflammatory mediators, in a dose-related manner. Conclusively, our data provide a novel implication of anti-nociceptive mechanism of melatonin in chemotherapy-related pain.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- i.p. :
-
Intraperitoneal
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MIP-1α:
-
Monocyte inflammatory protein-1
- NFκB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- PB:
-
Phosphate buffer
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PWL:
-
Paw withdrawal latency
- PWT:
-
Paw withdrawal threshold
- TLRs:
-
Toll-like receptors
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Agboola, S.O., W. Ju, A. Elfiky, J.C. Kvedar, and K. Jethwani. 2015. The effect of technology-based interventions on pain, depression, and quality of life in patients with cancer: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Medical Internet Research 17 (3): e65.
Ambriz-Tututi, M., H.I. Rocha-Gonzalez, S.L. Cruz, and V. Granados-Soto. 2009. Melatonin: a hormone that modulates pain. Life Sciences 84 (15–16): 489–498.
Areti, A., P. Komirishetty, M. Akuthota, R.A. Malik, and A. Kumar. 2017. Melatonin prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and promotes neuroprotection by inducing autophagy during oxaliplatin-evoked peripheral neuropathy. Journal of Pineal Research 62 (3).
Blask, D.E., R.T. Dauchy, L.A. Sauer, J.A. Krause, and G.C. Brainard. 2002. Light during darkness, melatonin suppression and cancer progression. Neuro Endocrinology Letters 23 (Suppl 2): 52–56.
Blask, D.E., L.A. Sauer, and R.T. Dauchy. 2002. Melatonin as a chronobiotic/anticancer agent: cellular, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms of action and their implications for circadian-based cancer therapy. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 2 (2): 113–132.
Carozzi, V.A., A. Canta, and A. Chiorazzi. 2015. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: what do we know about mechanisms? Neuroscience Letters 596: 90–107.
Cersosimo, R.J. 2005. Oxaliplatin-associated neuropathy: a review. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 39 (1): 128–135.
Chaplan, S.R., F.W. Bach, J.W. Pogrel, J.M. Chung, and T.L. Yaksh. 1994. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 53 (1): 55–63.
Chung, Y.H., and D. Kim. 2016. Enhanced TLR4 expression on colon cancer cells after chemotherapy promotes cell survival and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through phosphorylation of GSK3beta. Anticancer Research 36 (7): 3383–3394.
Di Cesare Mannelli, L., A. Pacini, L. Bonaccini, M. Zanardelli, T. Mello, and C. Ghelardini. 2013. Morphologic features and glial activation in rat oxaliplatin-dependent neuropathic pain. The Journal of Pain 14 (12): 1585–1600.
Di Cesare Mannelli, L., A. Pacini, L. Micheli, A. Tani, M. Zanardelli, and C. Ghelardini. 2014. Glial role in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain. Experimental Neurology 261: 22–33.
Ding, K., H. Wang, J. Xu, X. Lu, L. Zhang, and L. Zhu. 2014. Melatonin reduced microglial activation and alleviated neuroinflammation induced neuron degeneration in experimental traumatic brain injury: possible involvement of mTOR pathway. Neurochemistry International 76: 23–31.
Ebadi, M., P. Govitrapong, P. Phansuwan-Pujito, F. Nelson, and R.J. Reiter. 1998. Pineal opioid receptors and analgesic action of melatonin. Journal of Pineal Research 24 (4): 193–200.
El-Shenawy, S.M., O.M. Abdel-Salam, A.R. Baiuomy, S. El-Batran, and M.S. Arbid. 2002. Studies on the anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects of melatonin in the rat. Pharmacological Research 46 (3): 235–243.
Esposito, E., I. Paterniti, E. Mazzon, P. Bramanti, and S. Cuzzocrea. 2010. Melatonin reduces hyperalgesia associated with inflammation. Journal of Pineal Research 49 (4): 321–331.
Fu, J., X. Xia, Z. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, Q. Shi, X. Song, E. Song, and Y. Song. 2017. The acute exposure of tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone (a.k.a. chloranil) triggers inflammation and neurological dysfunction via toll-like receptor 4 signaling: the protective role of melatonin preconditioning. Toxicology 381: 39–50.
Gao, Y.J., and R.R. Ji. 2010. Targeting astrocyte signaling for chronic pain. Neurotherapeutics 7 (4): 482–493.
Gao, Y.J., L. Zhang, O.A. Samad, M.R. Suter, K. Yasuhiko, Z.Z. Xu, J.Y. Park, A.L. Lind, Q. Ma, and R.R. Ji. 2009. JNK-induced MCP-1 production in spinal cord astrocytes contributes to central sensitization and neuropathic pain. The Journal of Neuroscience 29 (13): 4096–4108.
Garcia-Perganeda, A., J.M. Guerrero, M. Rafii-El-Idrissi, M. Paz Romero, D. Pozo, and J.R. Calvo. 1999. Characterization of membrane melatonin receptor in mouse peritoneal macrophages: inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. Journal of Neuroimmunology 95 (1–2): 85–94.
Han, Y., and M.T. Smith. 2013. Pathobiology of cancer chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Frontiers in Pharmacology 4: 156.
Heiman, A., A. Pallottie, R.F. Heary, and S. Elkabes. 2014. Toll-like receptors in central nervous system injury and disease: a focus on the spinal cord. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 42: 232–245.
Hu, Y., Z. Wang, S. Pan, H. Zhang, M. Fang, H. Jiang, H. Zhang, et al. 2017. Melatonin protects against blood-brain barrier damage by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway after LPS treatment in neonatal rats. Oncotarget 8 (19): 31638–31654.
Ismail, S.A., and H.A. Mowafi. 2009. Melatonin provides anxiolysis, enhances analgesia, decreases intraocular pressure, and promotes better operating conditions during cataract surgery under topical anesthesia. Anesthesia and Analgesia 108 (4): 1146–1151.
Kawasaki, Y., L. Zhang, J.K. Cheng, and R.R. Ji. 2008. Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. The Journal of Neuroscience 28 (20): 5189–5194.
Kelland, L. 2007. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nature Reviews. Cancer 7 (8): 573–584.
Kiguchi, N., Y. Kobayashi, and S. Kishioka. 2012. Chemokines and cytokines in neuroinflammation leading to neuropathic pain. Current Opinion in Pharmacology 12 (1): 55–61.
Konturek, S.J., O. Zayachkivska, X.O. Havryluk, T. Brzozowski, Z. Sliwowski, M. Pawlik, P.C. Konturek, M. Czesnikiewicz-Guzik, M.R. Gzhegotsky, and W.W. Pawlik. 2007. Protective influence of melatonin against acute esophageal lesions involves prostaglandins, nitric oxide and sensory nerves. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 58 (2): 361–377.
Lin, S.H., Y.N. Huang, J.H. Kao, L.T. Tien, R.Y. Tsai, and C.S. Wong. 2016. Melatonin reverses morphine tolerance by inhibiting microglia activation and HSP27 expression. Life Sciences 152: 38–43.
Liu, T., Q. Han, G. Chen, Y. Huang, L.X. Zhao, T. Berta, Y.J. Gao, and R.R. Ji. 2016. Toll-like receptor 4 contributes to chronic itch, alloknesis, and spinal astrocyte activation in male mice. Pain 157 (4): 806–817.
Loiseau, F., C. Le Bihan, M. Hamon, and M.H. Thiebot. 2006. Effects of melatonin and agomelatine in anxiety-related procedures in rats: interaction with diazepam. European Neuropsychopharmacology 16 (6): 417–428.
Matsushita, K., H. Tozaki-Saitoh, C. Kojima, T. Masuda, M. Tsuda, K. Inoue, and S. Hoka. 2014. Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 is an important pathological regulator in the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology 120 (6): 1491–1503.
Raghavendra, V., J.N. Agrewala, and S.K. Kulkarni. 2000. Melatonin reversal of lipopolysacharides-induced thermal and behavioral hyperalgesia in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 395 (1): 15–21.
Robinson, C.R., H. Zhang, and P.M. Dougherty. 2014. Astrocytes, but not microglia, are activated in oxaliplatin and bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy in the rat. Neuroscience 274: 308–317.
Romero-Sandoval, E.A., R.J. Horvath, and J.A. DeLeo. 2008. Neuroimmune interactions and pain: focus on glial-modulating targets. Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs 9 (7): 726–734.
Sanchez-Barcelo, E.J., S. Cos, D. Mediavilla, C. Martinez-Campa, A. Gonzalez, and C. Alonso-Gonzalez. 2005. Melatonin-estrogen interactions in breast cancer. Journal of Pineal Research 38 (4): 217–222.
Scarabelot, V.L., L.F. Medeiros, C. de Oliveira, L.N. Adachi, I.C. de Macedo, S.G. Cioato, J.S. de Freitas, et al. 2016. Melatonin alters the mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia induced by orofacial pain model in rats. Inflammation 39 (5): 1649–1659.
Srinivasan, V., S.R. Pandi-Perumal, D.W. Spence, A. Moscovitch, I. Trakht, G.M. Brown, and D.P. Cardinali. 2010. Potential use of melatonergic drugs in analgesia: mechanisms of action. Brain Research Bulletin 81 (4–5): 362–371.
Sugden, D. 1983. Psychopharmacological effects of melatonin in mouse and rat. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 227 (3): 587–591.
Wang, Y.M., B.Z. Jin, F. Ai, C.H. Duan, Y.Z. Lu, T.F. Dong, and Q.L. Fu. 2012. The efficacy and safety of melatonin in concurrent chemotherapy or radiotherapy for solid tumors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 69 (5): 1213–1220.
Xin, W., W. Chun, L. Ling, and W. Wei. 2012. Role of melatonin in the prevention of morphine-induced hyperalgesia and spinal glial activation in rats: protein kinase C pathway involved. The International Journal of Neuroscience 122 (3): 154–163.
Yoon, S.Y., C.R. Robinson, H. Zhang, and P.M. Dougherty. 2013. Spinal astrocyte gap junctions contribute to oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hypersensitivity. The Journal of Pain 14 (2): 205–214.
Zhang, R.X., B. Liu, A. Li, L. Wang, K. Ren, J.T. Qiao, B.M. Berman, and L. Lao. 2008. Interleukin 1beta facilitates bone cancer pain in rats by enhancing NMDA receptor NR-1 subunit phosphorylation. Neuroscience 154 (4): 1533–1538.
Zimmermann, M. 1983. Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16 (2): 109–110.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grants from Medicine Health Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2017200948) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81471889).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Ye-song Wang and Yuan-yuan Li contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Sup Fig. 1
Immunostaining of primary cultured astrocytes with the astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). (JPEG 402 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Ys., Li, Yy., Cui, W. et al. Melatonin Attenuates Pain Hypersensitivity and Decreases Astrocyte-Mediated Spinal Neuroinflammation in a Rat Model of Oxaliplatin-Induced Pain. Inflammation 40, 2052–2061 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0645-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0645-y