Abstract
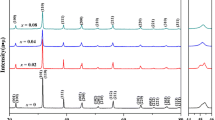
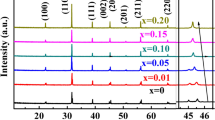
(1−x) BaTiO3–xBiYbO3 (abbreviated as (1−x) BT−xBY, x = 0, 0.03, 0.06 and 0.09) ferroelectric ceramics have been fabricated by conventional sintering (CS) and microwave sintering (MWS) methods. The microstructure, dielectric and ferroelectric properties of (1−x) BT–xBY ceramics have been investigated systematically. X-ray diffraction patterns indicate all samples possess single perovskite phase and the crystal structure transforms from tetragonal to pseudo-cubic phase with increasing x. It can be also found that denser microstructure and finer grains can be obtained by MWS compared to CS as indicated by scanning electron microscopy. Dielectric measurements reveal that the addition of BY can lead to an obvious relaxation behavior in all samples, and the relaxation characteristics of MWS samples are stronger than those of CS samples. Moreover, the dielectric constant decreases with increasing BY content and the temperature stability and frequency stability of dielectric properties can be enhanced by using MWS method and addition of BY. P–E hysteresis loops become slimmer with the increase of BY content, and the ferroelectric properties of MWS samples are similar to those of CS samples. The leakage current of MWS sample is smaller than that of CS sample from J–E curve. The energy storage efficiency (η) increases with increasing BY content, while the energy storage density (U) increases and then decreases, Umax is obtained at x = 0.06. These results demonstrate that MWS technique and moderate BY content are effective methods to prepare materials for energy storage application.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Song, S.J. Zhang, H.X. Liu, H. Hao, M.H. Cao, Q. Li, Q. Wang, Z.H. Yao, Z.J. Wang, M.T. Lanagan, Improved energy storage properties accompanied by enhanced interface polarization in annealed microwave-sintered BST. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 3212–3222 (2015)
A. Michaela, N. Beuerlein, T.M. Kumar, H. Usher, B. James, N. Shaklee, I.M. Raengthon, D.P. Reaney, J.L. Cann, G.L. Jones, Brennecka, Current understanding of structure–processing–property relationships in BaTiO3–Bi (M) O3 dielectrics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 2849–2870 (2016)
N. Kumar, D.P. Cann, Tailoring transport properties through nonstoichiometry in BaTiO3–BiScO3 and SrTiO3–Bi (Zn1/2Ti1/2) O3 for capacitor applications. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 9404–9414 (2016)
H. Ogihara, C.A. Randall, S. Trolier-Mckinstry, Weakly coupled relaxor behavior of BaTiO3–BiScO3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 110–118 (2009)
Y. Wang, Y.P. Pu, X. Li, H.Y. Zheng, Z.Y. Gao, Evolution from ferroelectric to diffused ferroelectric, and relaxor ferroelectric in BaTiO3–BiFeO3 solid solutions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 183, 247–253 (2016)
M. Liu, H. Hao, W. Chen, D. Zhou, M. Appiah, B. Liu, M. Cao, Z. Yao, H. Liu, Z. Zhang, Preparation and dielectric properties of X9R core–shell BaTiO3 ceramics coated by BiAlO3–BaTiO3. Ceram. Int. 42, 379–387 (2015)
M. Liu, H. Hao, W. Chen, D. Zhou, M. Appiah, B. Liu, M. Cao, Z. Yao, H. Liu, Z. Zhang, Temperature stability of dielectric properties for xBiAlO3–(1–x)BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 2303–2311 (2015)
H. Yu, Z.G. Ye, Dielectric properties and relaxor behavior of a new (1−x) BaTiO3–xBiAlO3 solid solution. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 034114 (2008)
S.Y. Zheng, E. Odendo, L.J. Liu, D.P. Shi, Y.M. Huang, L.L. Fan, J. Chen, L. Fang, B. Elouadi, Electrostrictive and relaxor ferroelectric behavior in BiAlO3-modified BaTiO3 lead-free ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 094102 (2013)
Z. Shen, X. Wang, B. Luo, L. Li, BaTiO3–BiYbO3 perovskite materials for energy storage application. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 18146–18153 (2015)
T. Strathdee, L. Luisman, A. Feteira, K. Reichmann, Ferroelectric-to-relaxor crossover in (1−x) BaTiO3−x BiYbO3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.08) ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 2292–2295 (2011)
Q.Y. Hu, L. Jin, T. Wang, C.C. Li, Z. Xing, X.Y. Wei, Dielectric and temperature stable energy storage properties of 0.88BaTiO3–0.12Bi(Mg1/2Ti1/2)O3 bulk ceramics. J. Alloy Comp. 640, 416–420 (2015)
Y.J. Wu, Y.H. Huang, N. Wang, J. Li, M.S. Fu, X.M. Chen, Effects of phase constitution and microstructure on energy storage properties of barium strontium titanate ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37, 2099–2104 (2017)
Y.P. Pu, L. Zhang, M.T. Yao, W.Y. Ge, M. Chen, Improved energy storage properties of microwave sintered 0.475BNT–0.525BCTZ–x wt% MgO ceramics. Mater. Lett. 189, 232–235 (2017)
R. Hayati, M.A. Bahrevar, T. Ebadzadeh, V. Rojas, N. Novak, J. Koruza, Effects of Bi2O3 additive on sintering process and dielectric, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 lead-free piezoceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 3391–3400 (2016)
P. Gao, Y.P. Pu, Y.R. Wu, P. Li, A comparative study on positive temperature coefficient effect of BaTiO3–K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ceramics by conventional and microwave sintering. Ceram. Int. 40, 637–642 (2014)
S. Hajra, S. Sahoo, M. De, P.K. Rout, H.S. Tewari, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural and electrical characteristics of barium modified bismuth-sodium titanate (Bi0.49Na0.49Ba0.02)TiO3. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 1463–1472 (2018)
S. Mahajan, O.P. Thakur, D.K. Bhattacharya, K. Sreenivas, A comparative study of Ba0.95Ca0.05Zr0.25Ti0.75O3 relaxor ceramics prepared by conventional and microwave sintering techniques. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 858–862 (2008)
M. Zhang, X.Y. Zhang, X.W. Qi, Y. Lia, L. Bao, Y.H. Gu, Effects of sintering temperature and composition on dielectric, ferroelectric, and magnetoelectric properties of BaTiO3–BiFeO3 solid solutions. Ceram. Int. 43, 16957–16964 (2017)
H. Ghayour, M. Abdellahi, A brief review of the effect of grain size variation on the electrical properties of BaTiO3-based ceramics. Powder Technol. 292, 84–93 (2016)
X.G. Tang, J. Wang, X.X. Wang, H.L.W. Chan, Effects of grain size on the dielectric properties and tunabilities of sol–gel derived Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 ceramics. Solid State Commun. 131, 163–168 (2004)
Y. Huan, X.H. Wang, J. Fang, L.T. Li, Grain size effect on piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 1445–1448 (2014)
G. Chen, X.D. Peng, C.L. Fu, W. Cai, R.L. Gao, P.G. Fan, X. Yi, H.Q. Yang, C. Ji, H.L. Yong, Effects of sintering method and BiFeO3 dopant on the dielectric and ferroelectric properties of BaTiO3–BiYbO3 based solid solution ceramics. Ceram. Int. 44, 16880–16889 (2018)
F. Zhang, L. Zhang, X. Guo, S. Yang, Q. Tian, S. Fan, The effect of sintering atmospheres on the properties of CSBT-0.15 ferroelectric ceramics. Ceram. Int. 44, 13502–13506 (2018)
A. Kupec, H. Ur, R.C. Frunza, E. Tchernychova, B. Mali, Microstructure-dependent leakage-current properties of solution-derived (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 thin films. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 3507–3511 (2015)
H. Borkar, V. Rao, M. Tomar, V. Gupta, A. Kumar, Near room temperature bismuth and lithium co-substituted BaTiO3 relaxor ferroelectrics family. J. Alloys Compd. 737, 821–828 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chongqing Research Program of Basic Research and Frontier Technology (Grant No. CSTC2018jcyjAX0416, CSTC2016jcyjA0175, CSTC2016jcyjA0349, CSTC2015jcyjA50003, CSTC2015jcyjA50015); Excellent Talent Project in University of Chongqing (Grant No. 2017-35); the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Social Undertakings and People’s Livelihood Guarantee of Chongqing (Grant No. CSTC2017shmsA0192) and the Program for Innovation Teams in University of Chongqing, China (Grant No. CXTDX201601032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose, and manuscript is approved by all authors and the institutes for publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Peng, X., Fu, C. et al. Microstructure, dielectric and ferroelectric properties of (1−x) BaTiO3–xBiYbO3 ceramics fabricated by conventional and microwave sintering methods. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 20017–20032 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0132-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0132-8