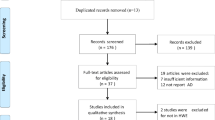
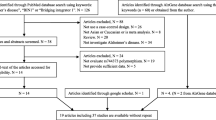
Abstract
The sorting-related receptor gene (SORL1) has been defined as an interesting candidate gene for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Recently, one novel variant, rs11218343, within SORL1 was reported to be related to late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD) in Caucasians, Korean, and Japanese. The aim of this case–control study is to investigate whether SORL1 rs11218343 contributes to susceptibility for LOAD in Chinese. Furthermore, our data, along with previously studies, were pooled for determining the risk of the rs11218343 polymorphism on LOAD. The rs11218343 polymorphism was genotyped in the 2350 independent subjects from Northern Han Chinese population (including 992 cases and 1358 age- and gender-matched controls). Result of the case–control study showed the association between rs11218343 polymorphism and the risk of LOAD in a Northern Han Chinese population (recessive model: odds ratio (OR) = 0.641, 95 % confidence interval (CI) = 0.464–0.884, P = 0.007; additive model: OR = 0.873, 95 % CI = 0.765–0.996, P = 0.043). The results of meta-analysis in subgroups (Caucasian and Asian) and the whole showed that the minor allele (C allele) within rs11218343 played a protective effect on AD risk (OR (95 % CI), 0.77 (0.72–0.83), 0.85 (0.79–0.91), 0.81 (0.76–0.85), respectively). In conclusion, the C allele in SORL1 rs11218343 may be a protective factor for LOAD in both Caucasian and Han Chinese.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertram L, Tanzi RE (2008) Thirty years of Alzheimer’s disease genetics: the implications of systematic meta-analyses. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(10):768–778. doi:10.1038/nrn2494
Gatz M, Reynolds CA, Fratiglioni L, Johansson B, Mortimer JA, Berg S, Fiske A, Pedersen NL (2006) Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63(2):168–174. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.2.168
Ashford JW, Mortimer JA (2002) Non-familial Alzheimer’s disease is mainly due to genetic factors. J Alzheimers Dis 4(3):169–177
Tan L, Yu JT, Zhang W, Wu ZC, Zhang Q, Liu QY, Wang W, Wang HF et al (2013) Association of GWAS-linked loci with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in a northern Han Chinese population. Alzheimers Dement 9(5):546–553. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.08.007
Lambert JC, Ibrahim-Verbaas CA, Harold D, Naj AC, Sims R, Bellenguez C, DeStafano AL, Bis JC et al (2013) Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 45(12):1452–1458. doi:10.1038/ng.2802
Naj AC, Jun G, Beecham GW, Wang LS, Vardarajan BN, Buros J, Gallins PJ, Buxbaum JD et al (2011) Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43(5):436–441. doi:10.1038/ng.801
Hollingworth P, Harold D, Sims R, Gerrish A, Lambert JC, Carrasquillo MM, Abraham R, Hamshere ML et al (2011) Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43(5):429–435. doi:10.1038/ng.803
Seshadri S, Fitzpatrick AL, Ikram MA, DeStefano AL, Gudnason V, Boada M, Bis JC, Smith AV et al (2010) Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci associated with Alzheimer disease. Jama 303(18):1832–1840. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.574
Rogaeva E, Meng Y, Lee JH, Gu Y, Kawarai T, Zou F, Katayama T, Baldwin CT et al (2007) The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet 39(2):168–177. doi:10.1038/ng1943
Yin RH, Yu JT, Tan L (2015) The role of SORL1 in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 51(3):909–918. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8742-5
Willnow TE, Petersen CM, Nykjaer A (2008) VPS10P-domain receptors— regulators of neuronal viability and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(12):899–909. doi:10.1038/nrn2516
Offe K, Dodson SE, Shoemaker JT, Fritz JJ, Gearing M, Levey AI, Lah JJ (2006) The lipoprotein receptor LR11 regulates amyloid beta production and amyloid precursor protein traffic in endosomal compartments. J Neurosci 26(5):1596–1603. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4946-05.2006
Mattson MP (2004) Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 430(7000):631–639. doi:10.1038/nature02621
Scherzer CR, Offe K, Gearing M, Rees HD, Fang G, Heilman CJ, Schaller C, Bujo H et al (2004) Loss of apolipoprotein E receptor LR11 in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 61(8):1200–1205. doi:10.1001/archneur.61.8.1200
Dodson SE, Gearing M, Lippa CF, Montine TJ, Levey AI, Lah JJ (2006) LR11/SorLA expression is reduced in sporadic Alzheimer disease but not in familial Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65(9):866–872. doi:10.1097/01.jnen.0000228205.19915.20
Miyashita A, Koike A, Jun G, Wang LS, Takahashi S, Matsubara E, Kawarabayashi T, Shoji M et al (2013) SORL1 is genetically associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in Japanese, Koreans and Caucasians. PLoS One 8(4):e58618. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058618
Yu JT, Ma XY, Wang YL, Sun L, Tan L, Hu N (1921) Tan L (2013) Genetic variation in clusterin gene and Alzheimer’s disease risk in Han Chinese. Neurobiol Aging 34(7):e1917–1923. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.01.010
Liu QY, Yu JT, Miao D, Ma XY, Wang HF, Wang W, Tan L (2013) An exploratory study on STX6, MOBP, MAPT, and EIF2AK3 and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 34(5):1519–1517. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.10.004, e1513-1517
Tan MS, Yu JT, Jiang T, Zhu XC, Wang HF, Zhang W, Wang YL, Jiang W et al (2013) NLRP3 polymorphisms are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in Han Chinese. J Neuroimmunol 265(1-2):91–95. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.10.002
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34(7):939–944
Stang A (2010) Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 25(9):603–605. doi:10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
Dumanis SB, Burgert T, Caglayan S, Fuchtbauer A, Fuchtbauer EM, Schmidt V, Willnow TE (2015) Distinct functions for anterograde and retrograde sorting of SORLA in amyloidogenic processes in the brain. J Neurosci 35(37):12703–12713. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0427-15.2015
Andersen OM, Reiche J, Schmidt V, Gotthardt M, Spoelgen R, Behlke J, von Arnim CA, Breiderhoff T et al (2005) Neuronal sorting protein-related receptor sorLA/LR11 regulates processing of the amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(38):13461–13466. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503689102
Schmidt V, Sporbert A, Rohe M, Reimer T, Rehm A, Andersen OM, Willnow TE (2007) SorLA/LR11 regulates processing of amyloid precursor protein via interaction with adaptors GGA and PACS-1. J Biol Chem 282(45):32956–32964. doi:10.1074/jbc.M705073200
Caglayan S, Takagi-Niidome S, Liao F, Carlo AS, Schmidt V, Burgert T, Kitago Y, Fuchtbauer EM et al (2014) Lysosomal sorting of amyloid-beta by the SORLA receptor is impaired by a familial Alzheimer’s disease mutation. Sci Transl Med 6(223):223ra220. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007747
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81471309, 81371406, 81571245, and 81501103), Shandong Provincial Outstanding Medical Academic Professional Program, Qingdao Key Health Discipline Development Fund, Qingdao Outstanding Health Professional Development Fund, and Shandong Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center for Neurodegenerative Disorders.
Conflict of Interest
The authors disclose that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Cheng-Cheng Zhang and Hui-Fu Wang are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, CC., Wang, HF., Tan, MS. et al. SORL1 Is Associated with the Risk of Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease: a Replication Study and Meta-Analyses. Mol Neurobiol 54, 1725–1732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9780-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9780-y