Abstract
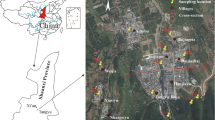
Hydrochemical investigations were conducted to determine the chemical composition of groundwater in the Sangong River Watershed (SRW), Northwestern China. Thirty-two groundwater samples were collected from different wells to monitor the water chemistry of various ions. The results of the chemical analysis indicate that the groundwater in the area is generally neutral to slightly alkaline and predominantly contains Ca2+ and Mg2+ cations as well as HCO3 − and SO4 2+ anions. The Na++K+ concentration increases from the alluvial–diluvial fan to alluvial plain. TDS values are becoming larger along the direction of the groundwater flow in general because long residence time and evaporation. The contribution of Na++K+ to the major cations which have been affected by water–rock interactions has great uncertainty. High positive correlations were obtained among the following ions: SO4 2−–Mg2+, SO4 2−–Na++K+, Cl−–Mg2+, Cl–Na++K+, Mg2+–Na++K+ and SO4 2−–Cl−. The dominant hydrochemical facies is Ca2+–Mg2+–HCO3 −, which is in relation with their interaction with the geological formations of the basin, cation exchange between groundwater and clay minerals and anthropogenic activities. The saturation index (SI) indicates that the gypsum-halite dissolution reactions occur during a certain degree of rock weathering. Almost all SI values of anhydrite are less than zero which shows that it remains unsaturated with respect to these minerals. That is to say, those carbonate mineral phases may have influenced the chemical composition of the study area. According to the Wilcox, US Salinity Laboratory and residual sodium carbonate (RSC) classifications, most of the groundwater samples in the study area are suitable for irrigation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams S, Titus R, Pietersen K, Tredoux G, Harris C (2001) Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. J Hydrol 241:91–103. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00370-X
Adomako D, Osae S, Akiti TT, Faye S, Maloszewski P (2011) Geochemical and isotopic studies of groundwater conditions in the Densu River Basin of Ghana. Environ Earth Sci 62:1071–1084. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0595-2
Aghazadeh N, Mogaddam AA (2011) Investigation of hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Harzandat aquifer, Northwest of Iran. Environ Monit Assess 176:183–195. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1575-4
Banoeng-Yakubo B, Yidana S, Nti E (2009) An evaluation of the genesis and suitability of groundwater for irrigation in the Volta Region, Ghana. Environ Geol 57:1005–1010. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1385-y
Capell R, Tetzlaff D, Malcolm IA, Hartley AJ, Soulsby C (2011) Using hydrochemical tracers to conceptualise hydrological function in a larger scale catchment draining contrasting geologic provinces. J Hydrol 408:164–177. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.07.034
Cloutier V, Lefebvre R, Therrien R, Savard MM (2008) Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. J Hydrol 353:294–313. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.02.015
Dar I, Sankar K, Dar M (2011) Spatial assessment of groundwater quality in Mamundiyar basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 178:437–447. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1702-2
Deutsch JW (1997) Groundwater Geochemistry¸ Fundamentals and Application to Contamination. Lewis Publishers, CRC, Boca Raton, p 222
Giridharan L, Venugopal T, Jayaprakash M (2010) Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes on river Cooum, South India. Environ Monit Assess 162:277–289. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0795-y
Han D, Liang X, Jin M, Currell M, Han Y, Song X (2009) Hydrogeochemical indicators of groundwater flow systems in the Yangwu River Alluvial Fan, Xinzhou Basin, Shanxi, China. Environ Manage 44:243–255. doi:10.1007/s00267-009-9301-0
Han DM, Liang X, Jin MG, Currell MJ, Song XF, Liu CM (2010) Evaluation of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and mixing behavior in the daying and Qicun geothermal systems, Xinzhou Basin. J Volcanol Geoth Res 189:92–104. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2009.10.011
Hu K, Huang Y, Li H, Li B, Chen D, White RE (2005) Spatial variability of shallow groundwater level, electrical conductivity and nitrate concentration, and risk assessment of nitrate contamination in North China Plain. Environ Int 31:896–903. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.05.028
Jalali M (2007) Assessment of the chemical components of Famenin groundwater, western Iran. Environ Geochem Health 29:357–374. doi:10.1007/s10653-006-9080-y
Kharaka YK, Hanor JS(2003)Deep fluids in the continents: I. sedimentary basins. Treatise on geochemistry, vol 5. In: Drever JI (ed), Holland HD, Turekian KK (executive eds). Elsevier, ISBN 0-08-043751-6, pp 499–540, 605. doi:10.1016/B0-08-043751-6/05085-4
Kis B-M, Czellecz B, Baciu C, Kékedy-Nagy L (2012) Hydrogeochemical features of some mineral waters at the contact between Harghita Mts. (Eastern Carpathians) and the Transylvanian Basin. Procedia Environ Sci 14:195–206. doi:10.1016/j.proenv.2012.03.019
Kumar M, Ramanathan AL, Rao MS, Kumar B (2006) Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India. Environ Geol 50:1025–1039. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0275-4
Kumar SK, Rammohan V, Sahayam JD, Jeevanandam M (2009) Assessment of groundwater quality and hydrogeochemistry of Manimuktha River basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 159:341–351. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0633-7
Lu Y, Tang C, Chen J, Song X, Li F, Sakura Y (2008) Spatial characteristics of water quality, stable isotopes and tritium associated with groundwater flow in the Hutuo River alluvial fan plain of the North China Plain. Hydrogeol J 16:1003–1015. doi:10.1007/s10040-008-0292-3
Luo GP, Zhou CH, Chen X, Li Y (2008) A methodology of characterizing status and trend of land changes in oases: a case study of SRW, Xinjiang, China. J Environ Manage 88:775–783. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.04.003
Mahlknecht J, Steinich B, Navarro de León I (2004) Groundwater chemistry and mass transfers in the Independence aquifer, central Mexico, by using multivariate statistics and mass-balance models. Environ Geol 45:781–795. doi:10.1007/s00254-003-0938-3
Namaghi H, Karami G, Saadat S (2011) A study on chemical properties of groundwater and soil in ophiolitic rocks in Firuzabad, east of Shahrood, Iran: with emphasis to heavy metal contamination. Environ Monit Assess 174:573–583. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1479-3
Palma P, Alvarenga P, Palma V, Fernandes R, Soares AVM, Barbosa I (2010) Assessment of anthropogenic sources of water pollution using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Alqueva’s reservoir, Portugal. Environ Monit Assess 165:539–552. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0965-y
Parkhurst DL, and CAJ Appelo (1999) Users’ guide to PHREEQC (Version 2). U.S. Geological Survey, Water Resources Investigations Report 99–4259, Denver, Colorado
Purushotham D, Prakash MR, Narsing Rao A (2011) Groundwater depletion and quality deterioration due to environmental impacts in Maheshwaram watershed of R.R. district, AP (India). Environ Earth Sci 62:1707–1721. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0666-4
Ravikumar P, Venkatesharaju K, Somashekar RK (2010) Major ion chemistry and hydrochemical studies of groundwater of Bangalore South Taluk, India. Environ Monit Assess 163:643–653. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0865-1
Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline alkali soils: agriculture, vol 160. Handbook 60. US Department of Agriculture, Washington
Saeedi M, Abessi O, Sharifi F, Meraji H (2010) Development of groundwater quality index. Environ Monit Assess 163:327–335. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0837-5
Sharma A, Singh A, Kumar K (2012) Environmental geochemistry and quality assessment of surface and subsurface water of Mahi River basin, western India. Environ Earth Sci 65:1231–1250. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1371-7
Stamatis G, Alexakis D, Gamvroula D, Migiros G (2011) Groundwater quality assessment in Oropos-Kalamos basin, Attica, Greece. Environ Earth Sci 64:973–988. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-0914-2
Subba Rao N (2008) Factors controlling the salinity in groundwater in parts of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 138:327–341. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9801-4
Suthar S, Sharma J, Chabukdhara M, Nema A (2010) Water quality assessment of river Hindon at Ghaziabad, India: impact of industrial and urban wastewater. Environ Monit Assess 165:103–112. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0930-9
Tank D, Chandel CPS (2010) A hydrochemical elucidation of the groundwater composition under domestic and irrigated land in Jaipur City. Environ Monit Assess 166:69–77. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0985-7
USSL (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of salinity and alkaline soil. USDA Hand Book No. 60, Washington
Vanderzalm JL, Jeuken BM, Wischusen JDH, Pavelic P, La Salle CLG, Knapton A, Dillon PJ (2011) Recharge sources and hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in alluvial basins in arid central Australia. J Hydrol 397:71–82. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.11.035
Wang P, Yu J, Zhang Y, Liu C (2013) Groundwater recharge and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Ejina Basin, northwest China. J Hydrol 476:72–86. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.10.049
WHO (2006) Guidelines for drinking water quality. 1. Recommendations, 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation water. USDA Circular, Washington, p 969
Yidana S, Ophori D, Banoeng-Yakubo B (2008) Hydrogeological and hydrochemical characterization of the Voltaian Basin: the Afram Plains area, Ghana. Environ Geol 53:1213–1223. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0710-1
Yidana SM, Banoeng-Yakubo B, Akabzaa T, Asiedu D (2011) Characterization of the groundwater flow regime and hydrochemistry of groundwater from the Buem formation, Eastern Ghana. Hydrol Process 25:2288–2301. doi:10.1002/hyp.7992
Zhao C, Wang Y, Hu S, Li Y (2004) Effects of spatial variability on estimation of evapotranspiration in the continental river basin. J Arid Environ 56:373–382. doi:10.1016/S0140-1963(03)00040-5
Zhao C, Wang Y, Chen X, Li B (2005) Simulation of the effects of groundwater level on vegetation change by combining FEFLOW software. Ecol Model 187:341–351. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2004.10.019
Zhu GF, Li ZZ, Su YH, Ma JZ, Zhang YY (2007) Hydrogeochemical and isotope evidence of groundwater evolution and recharge in Minqin Basin, Northwest China. J Hydrol 333:239–251. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.08.013
Zhu GF, Su YH, Feng Q (2008) The hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater and surface water in the Heihe River Basin, northwest China. Hydrogeol J 16:167–182. doi:10.1007/s10040-007-0216-7
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 860540) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 91125010). The authors wish to thank the anonymous reviewers for their suggestions and critical comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, H. Major ion chemistry of groundwater in the Sangong River Watershed, Northwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 75, 487 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5321-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5321-2