Abstract
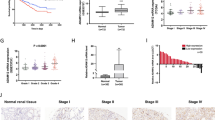
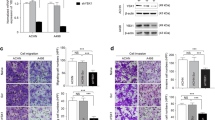
Discoidin domain receptor I (DDR1) is confirmed as a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), which plays a consequential role in a variety of cancers. Nevertheless, the influence of DDR1 expression and development in renal clear cell carcinoma (RCCC) are still not well corroborated. In our research, we firstly discovered that the expression level of DDR1 was remarkable related to TNM stage (p = 0.032), depth of tumor invasion (p = 0.047), and lymph node metastasis (p = 0.034) in 119 RCCC tissue samples using tissue microarray. The function of DDR1 was then evaluated in vitro using collagen I and DDR1 small interfering RNA (siRNA) to regulate the expression of DDR1 in OS-RC-2 and ACHN renal cancer cells (RCC). DDR1 expression correlated with increased RCC cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. Further study revealed that high expression of DDR1 can result in epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) activation. Western blot assay showed that the N-cadherin protein and vimentin were induced while E-cadherin was reduced after DDR1 over expression. Our results suggest that DDR1 is both a prognostic marker for RCCC and a potential functional target for therapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K, Mariotto A, Smith T, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:220–41.
Finley DS, Pantuck AJ, Belldegrun AS. Tumor biology and prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma. Oncologist. 2011;16 Suppl 2:4–13.
Coppin C, Kollmannsberger C, Le L, Porzsolt F, Wilt TJ. Targeted therapy for advanced renal cell cancer (rcc): a cochrane systematic review of published randomised trials. BJU Int. 2011;108:1556–63.
Valiathan RR, Marco M, Leitinger B, Kleer CG, Fridman R. Discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases: new players in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012;31:295–321.
Vogel W, Gish GD, Alves F, Pawson T. The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases are activated by collagen. Mol Cell. 1997;1:13–23.
Shrivastava A, Radziejewski C, Campbell E, Kovac L, McGlynn M, Ryan TE, et al. An orphan receptor tyrosine kinase family whose members serve as nonintegrin collagen receptors. Mol Cell. 1997;1:25–34.
Vogel WF, Abdulhussein R, Ford CE. Sensing extracellular matrix: an update on discoidin domain receptor function. Cell Signal. 2006;18:1108–16.
Yamanaka R, Arao T, Yajima N, Tsuchiya N, Homma J, Tanaka R, et al. Identification of expressed genes characterizing long-term survival in malignant glioma patients. Oncogene. 2006;25:5994–6002.
Johansson FK, Goransson H, Westermark B. Expression analysis of genes involved in brain tumor progression driven by retroviral insertional mutagenesis in mice. Oncogene. 2005;24:3896–905.
Heinzelmann-Schwarz VA, Gardiner-Garden M, Henshall SM, Scurry J, Scolyer RA, Davies MJ, et al. Overexpression of the cell adhesion molecules ddr1, claudin 3, and ep-cam in metaplastic ovarian epithelium and ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2004;10:4427–36.
Weiner HL, Huang H, Zagzag D, Boyce H, Lichtenbaum R, Ziff EB. Consistent and selective expression of the discoidin domain receptor-1 tyrosine kinase in human brain tumors. Neurosurgery. 2000;47:1400–9.
Park HS, Kim KR, Lee HJ, Choi HN, Kim DK, Kim BT, et al. Overexpression of discoidin domain receptor 1 increases the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in association with matrix metalloproteinase. Oncol Rep. 2007;18:1435–41.
Edwards DR, Murphy G. Cancer. Proteases—invasion and more. Nature. 1998;394:527–8.
Yoshimoto M, Itoh F, Yamamoto H, Hinoda Y, Imai K, Yachi A. Expression of mmp-7(pump-1) mrna in human colorectal cancers. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 1993;54:614–8.
Senota A, Itoh F, Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Hinoda Y, Imai K. Relation of matrilysin messenger rna expression with invasive activity in human gastric cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1998;16:313–21.
Uhm JH, Dooley NP, Villemure JG, Yong VW. Glioma invasion in vitro: regulation by matrix metalloprotease-2 and protein kinase c. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1996;14:421–33.
Mikami S, Oya M, Mizuno R, Kosaka T, Katsube K, Okada Y. Invasion and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Med Mol Morphol. 2014;47:63–7.
Sato A, Nagase H, Obinata D, Fujiwara K, Fukuda N, Soma M, et al. Inhibition of mmp-9 using a pyrrole-imidazole polyamide reduces cell invasion in renal cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2013;43:1441–6.
Lu H, Yang Z, Zhang H, Gan M, Zhou T, Wang S. The expression and clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase 7 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases 2 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 2013;5:890–6.
Thiery JP. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:740–6.
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 2006;172:973–81.
Shintani Y, Fukumoto Y, Chaika N, Svoboda R, Wheelock MJ, Johnson KR. Collagen i-mediated up-regulation of n-cadherin requires cooperative signals from integrins and discoidin domain receptor 1. J Cell Biol. 2008;180:1277–89.
Borza CM, Pozzi A. Discoidin domain receptors in disease. Matrix Biol J Int Soc Matrix Biol. 2014;34:185–92.
L’Hote CG, Thomas PH, Ganesan TS. Functional analysis of discoidin domain receptor 1: effect of adhesion on ddr1 phosphorylation. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol. 2002;16:234–6.
Alves F, Saupe S, Ledwon M, Schaub F, Hiddemann W, Vogel WF. Identification of two novel, kinase-deficient variants of discoidin domain receptor 1: differential expression in human colon cancer cell lines. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol. 2001;15:1321–3.
Sanchez MP, Tapley P, Saini SS, He B, Pulido D, Barbacid M. Multiple tyrosine protein kinases in rat hippocampal neurons: Isolation of ptk-3, a receptor expressed in proliferative zones of the developing brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:1819–23.
Johnson JD, Edman JC, Rutter WJ. A receptor tyrosine kinase found in breast carcinoma cells has an extracellular discoidin i-like domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:5677–81.
Laval S, Butler R, Shelling AN, Hanby AM, Poulsom R, Ganesan TS. Isolation and characterization of an epithelial-specific receptor tyrosine kinase from an ovarian cancer cell line. Cell Growth Differ Mol Biol J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 1994;5:1173–83.
Vogel WF, Aszodi A, Alves F, Pawson T. Discoidin domain receptor 1 tyrosine kinase has an essential role in mammary gland development. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:2906–17.
Alves F, Vogel W, Mossie K, Millauer B, Hofler H, Ullrich A. Distinct structural characteristics of discoidin i subfamily receptor tyrosine kinases and complementary expression in human cancer. Oncogene. 1995;10:609–18.
Miao L, Zhu S, Wang Y, Li Y, Ding J, Dai J, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 is associated with poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cell invasion via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Med Oncol. 2013;30:626.
Toy KA, Valiathan RR, Nunez F, Kidwell KM, Gonzalez ME, Fridman R, et al. Tyrosine kinase discoidin domain receptors ddr1 and ddr2 are coordinately deregulated in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;150:9–18.
Huo Y, Yang M, Liu W, Yang J, Fu X, Liu D, et al. High expression of ddr1 is associated with the poor prognosis in Chinese patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR. 2015;34:88.
Rudra-Ganguly N, Lowe C, Mattie M, Chang MS, Satpayev D, Verlinsky A, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 contributes to tumorigenesis through modulation of tgfbi expression. PLoS One. 2014;9, e111515.
Hou G, Vogel W, Bendeck MP. The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase ddr1 in arterial wound repair. J Clin Invest. 2001;107:727–35.
Ruiz PA, Jarai G. Collagen i induces discoidin domain receptor (ddr) 1 expression through ddr2 and a jak2-erk1/2-mediated mechanism in primary human lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:12912–23.
Maeda M, Johnson KR, Wheelock MJ. Cadherin switching: essential for behavioral but not morphological changes during an epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:873–87.
Kang Y, Massague J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and metastasis. Cell. 2004;118:277–9.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139:871–90.
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z, Kong D. Pancreatic cancer stem cells and emt in drug resistance and metastasis. Minerva Chir. 2009;64:489–500.
Battaglia S, Benzoubir N, Ghigna MR, Guettier C, Brechot C, Bourgeade MF. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Pathol. 2009;29(Spec No 1):S65–6.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407:249–57.
Ferrara N, Alitalo K. Clinical applications of angiogenic growth factors and their inhibitors. Nat Med. 1999;5:1359–64.
Weis SM, Cheresh DA. Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med. 2011;17:1359–70.
Cao YEG, Wang E, Pal K, Dutta SK, Bar-Sagi D, Mukhopadhyay D. Vegf exerts an angiogenesis-independent function in cancer cells to promote their malignant progression. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3912–8.
Reel B, Korkmaz CG, Arun MZ, Yildirim G, Ogut D, Kaymak A, et al. The regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression and the role of discoidin domain receptor 1/2 signalling in zoledronate-treated pc3 cells. J Cancer. 2015;6:1020–9.
Fu HL, Sohail A, Valiathan RR, Wasinski BD, Kumarasiri M, Mahasenan KV, et al. Shedding of discoidin domain receptor 1 by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:12114–29.
Castro-Sanchez L, Soto-Guzman A, Guaderrama-Diaz M, Cortes-Reynosa P, Salazar EP. Role of ddr1 in the gelatinases secretion induced by native type iv collagen in mda-mb-231 breast cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2011;28:463–77.
Kim HG, Tan L, Weisberg EL, Liu F, Canning P, Choi HG, et al. Discovery of a potent and selective ddr1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. ACS Chem Biol. 2013;8:2145–50.
Carafoli F, Mayer MC, Shiraishi K, Pecheva MA, Chan LY, Nan R, et al. Structure of the discoidin domain receptor 1 extracellular region bound to an inhibitory fab fragment reveals features important for signaling. Structure. 2012;20:688–97.
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), No.81301806; Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds, No.1501060A; six talent peaks project in Jiangsu Province, No.WSW-056.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Jingyuan Song and Xiao Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Chen, X., Bai, J. et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1), a promising biomarker, induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37, 11509–11521 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5021-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5021-2