Abstract
Background
Endoscopic cystocisternotomy is one of three surgical methods used to treat middle cranial fossa arachnoid cysts. There is debate about which method is the best.
Objective
The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of endoscopic cystocisternotomy for treatment of arachnoid cysts of the middle cranial fossa.
Methods
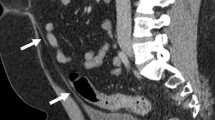
Thirty-two patients with arachnoid cysts of the middle cranial fossa who had undergone endoscopic cystocisternal fenestration between 2004 and 2009 were studied retrospectively. Data were obtained on clinical and neuroradiological presentation, indications to treat, surgical technique, complications, and the results of clinical and neuroradiological follow-up.
Results
Among the 27 patients with symptoms before surgery, 8 had disappearance of symptoms and 17 had improvement of symptoms. The cyst was reduced in size or it completely disappeared in 24 (75%) patients. The incidence rate of complications was 18.8%.
Conclusions
Endoscopic cystocisternal fenestration is an effective treatment for symptomatic arachnoid cysts of the middle cranial fossa and should be the initial surgical procedure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque FC, Giannotta SL (1997) Arachnoid cyst rupture producing subdural hygroma and intracranial hypertension: case reports. Neurosurgery 41:951–955
Helland CA, Wester K (2006) A population based study of intracranial arachnoid cysts: clinical and neuroimaging outcomes following surgical cyst decompression in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 105(5 Suppl):385–390
Balsubramaniam C, Laurent J, Rouah E et al (1989) Congenital arachnoid cysts in children. Pediatr Neurosci 15:223–228
Passero S, Filosomi G, Cioni R et al (1990) Arachnoid cysts of the middle cranial fossa: a clinical, radiological and followup study. Acta Neurol Scand 82:94–100
Santamarta D, Aguas J, Ferrer E (1995) The natural history of arachnoid cysts: endoscopic and cine-mode MRI evidence of a slit-valve mechanism. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 38:133–137
Von Wild K, Gullotta F (1987) Arachnoid cyst of the middle cranial fossa—aplasia of temporal lobe? Childs Nerv Syst 3:232–234
Levy ML, Wang M, Aryan HE et al (2003) Microsurgical keyhole approach for middle fossa arachnoid cyst fenestration. Neurosurgery 53:1138–1144, discussion 1144–5
Arroyo S, Santamaria J (1997) What is the relationship between arachnoid cysts and seizure foci? Epilepsia 38:1098–1102
Choi JU, Kim DS, Huh R (1999) Endoscopic approach to arachnoid cyst. Childs Nerv Syst 15:285–291
Wester K, Helland CA (2008) How often do chronic extra-cerebral haematomas occur in patients with intracranial arachnoid cysts? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 79:72–75
Parsch CS, Krauss J, Hofmann E et al (1997) Arachnoid cysts associated with subdural hematomas and hygromas: analysis of 16 cases, long-term follow up, and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 40:483–490
Martinez-Lage JF, Valenti JA, Piqueras C et al (2006) Functional assessment of intracranial arachnoid cysts with TC99 m-HMPAO SPECT: a preliminary report. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1091–1097
Sgouros S, Chapman S (2001) Congenital middle fossa arachnoid cysts may cause global brain ischaemia: a study with 99Tc-hexamethylpropyleneamineoxime single photon emission computerised tomography scans. Pediatr Neurosurg 35:188–194
Wester K, Hugdahl K (2003) Verbal laterality and handedness in patients with intracranial arachnoid cysts. J Neurol 250:36–41
Spacca B, Kandasamy J, Mallucci CL et al (2010) Endoscopic treatment of middle fossa arachnoid cysts: a series of 40 patients treated endoscopically in two centres. Childs Nerv Syst 26:163–172
Moon KS, Lee JK, Kim JH et al (2007) Spontaneous disappearance of a suprasellar arachnoid cyst: case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 23:99–104
Greenfield JP, Souweidane MM (2005) Endoscopic management of intracranial cysts. Neurosurg Focus 19:E7
Shim KW, Lee YH, Park EK et al (2009) Treatment option for arachnoid cysts. Childs Nerv Syst 25:1459–1466
Nowosławska E, Polis L, Kaniewska D et al (2006) Neuroendoscopic techniques in the treatment of arachnoid cysts in children and comparison with other operative methods. Childs Nerv Syst 22:599–604
Galassi E, Tognetti F, Gaist G et al (1982) CT scan and medtrizamide CT cisternography in arachnoid cysts of the middle cranial fossa: classification and pathophysiological aspects. Surg Neurol 17:363–369
Di Rocco C (2010) Sylvian fissure arachnoid cysts: we do operate on them but should it be done? Childs Nerv Syst 26:173–175
Di Rocco F, James SR, Roujeau T et al (2010) Limits of endoscopic treatment of sylvian arachnoid cysts in children. Childs Nerv Syst 26:155–162
Arai H, Sato K, Wachi A et al (1996) Arachnoid cysts of the middle cranial fossa: experience with 77 patients who were treated with cystoperitoneal shunting. Neurosurgery 39:1108–1112
Kamikawa S, Inui A, Tamaki N et al (2001) Application of flexible neuroendoscopes to intracerebroventricular arachnoid cysts in children: use of videoscopes. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 44:186–189
Kabil MS, Shahinian HK (2007) Fully endoscopic supraorbital resection of congenital middle cranial fossa arachnoid cysts: report of 2 cases. Pediatr Neurosurg 43:316–322
Oertel JM, Baldauf J, Schroeder HW et al (2009) Endoscopic cystoventriculostomy for treatment of paraxial arachnoid cysts. J Neurosurg 110(4):792–799
Elhammady MS, Bhatia S, Ragheb J (2007) Endoscopic fenestration of middle fossa arachnoid cysts: a technical description and case series. Pediatr Neurosurg 43:209–215
Karabatsou K, Hayhurst C, Buxton N et al (2007) Endoscopic management of arachnoid cysts: an advancing technique. J Neurosurg 106(6 Suppl):455–462
Conflict of interests
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gui, Sb., Wang, Xs., Zong, Xy. et al. Assessment of endoscopic treatment for middle cranial fossa arachnoid cysts. Childs Nerv Syst 27, 1121–1128 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1399-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1399-8