Abstract
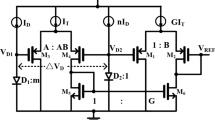
This paper proposed a new high-order curvature compensation technique for a new bandgap voltage reference structure using the temperature characteristics of current gain β and emitter bandgap narrowing factor ΔE G of a lateral NPN bipolar transistor. The new structure can produce two voltage references, which are 1.209 and 2.418 V, respectively. The simulation results show that the temperature coefficients of the two output voltage are 0.52 ppm/°C, the PSRR is more than 60 dB for frequencies at 10 kHz, and the circuit dissipates 0.18 mW with 5-V supply.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rincon-Mora, G. A. (2001). Voltage references from diodes to precision high-order bandgap circuits. New York: Wiley-IEEE Press.
Leung, K. N., & Mok, P. K. T. (2002). A Sub-1-v 15-ppm/°C CMOS Bandgap voltage reference without requiring low threshold voltage device. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37(4), 526–530. doi:10.1109/4.991391.
Leung, C. Y., Leung, K. N., & Mok, P. K. T. (2004). Design of a 1.5-V high-order curvature-compensated CMOS bandgap reference. Proceedings of the 2004 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (Vol. 1, pp. 48–52). doi:10.1109/ISCAS.2004.1328128.
Rincon-Mora, G. A., & Allen, P. E. (1994). A 1.1 V current-mode and piecewise linear curvature corrected bandgap reference. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuit, 33(10), 1551–1554.
Popa, C. (2005). CMOS logarithmic curvature-corrected voltage reference using a multiple differential structure. In ISSCS 2005 International Symposium on Signals, Circuits and Systems (Vol. 2, pp. 413–416).
Ahuja, B. K., Vu, H., Laber, C. A., & Owen, W. H. (2005). A very high precision 500-nA CMOS floating-gate analog voltage reference. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(12), 2364–2372. doi:10.1109/JSSC.2005.856268.
Lee, I., Kim, G., & Kim, W. (1994). Exponential curvature-compensated BiCMOS bandgap references. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuit, 29(11), 1396–1403. doi:10.1109/4.328634.
Dillard, W. C., & Jaeger, R. C. (1987). The temperature dependence of the amplification factor of bipolar-junction transistor. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 34, 139–142. doi:10.1109/T-ED.1987.22896.
Lindholm, F. A., & Hamilton, D. J. (1971). Incorporation of the early effect in the Ebers-Moll model. Proceedings of the IEEE, 59, 1377–1378. doi:10.1109/PROC.1971.8435.
Jaeger, R. C., & Brodersen, A. J. (1997). Self consistent bipolar transistor modes for computer simulation. Solid-State Electronics, 21, 1269–1272. doi:10.1016/0038-1101(78)90377-5.
Lanyon, H. P. D., & Tuft, R. A. (1978). Bandgap narrowing in heavily doped silicon. International Electron Devices Meeting, 24, 316–319.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, Z., Luo, P. et al. A 0.52 ppm/°C high-order temperature-compensated voltage reference. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 62, 17–21 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-009-9317-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-009-9317-7