Abstract
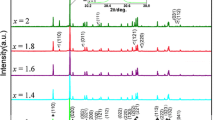
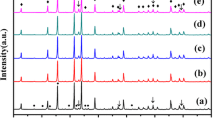
A series of 2.5ZnO–(5−x)TiO2–xZrO2–2.5Nb2O5 (abbreviated as ZTZN, 0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.4) composite ceramics were prepared by a solid state reaction method. The phase composition and microwave dielectric properties of the ceramics were investigated. X-ray diffraction patterns displayed the coexistence of ZnTiNb2O8 and Zn0.17Nb0.33Ti0.5O2 phases. With increasing the sintering temperature, the bulk density (ρ), permittivity (ε r ) and temperature coefficient of resonator frequency (τ f ) increased. With increasing the ZrO2 content, the ρ firstly increased and then decreased, Q × f value increased, ε r and τ f value decreased. Importantly, the τ f value of ZTZN ceramics (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.4) could be adjusted to near-zero. The 2.5ZnO–4.7TiO2–0.3ZrO2–2.5Nb2O5 ceramics sintered at 1075 °C exhibited the best comprehensive performances of Q × f = 30,155 GHz, ε r = 44 and τ f = 0.89 ppm/°C, indicating that they are candidates for microwave devices.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.Y. Zou, Z.H. Chen, X.K. Lan, W.Z. Lu, B. Ullah, X.H. Wang, W. Lei, Weak ferroelectricity and low-permittivity microwave dielectric properties of Ba2Zn(1+x)Si2O(7+x) ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37, 3065–3071 (2017)
H.F. Zhou, J. Huang, X.H. Tan, Microwave dielectric properties of low-permittivity CaMgSiO4 ceramic. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 15258–15262 (2017)
J. Guo, D. Zhou, H. Wang, Microwave dielectric properties of (1-x)ZnMoO4-xTiO2 composite ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 5863–5865 (2011)
Z.G. Zang, X.S. Tang, Enhanced fluorescence imaging performance of hydrophobic colloidal ZnO nanoparticles by a facile method. J. Alloys Compd. 619, 98–101 (2015)
C.L. Huang, M.H. Weng, Improved high Q value of MgTiO3-CaTiO3 microwave dielectric ceramics at low sintering temperature. Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 2741–2750 (2001)
R. Freer, Microwave dielectric ceramics: an overview. Silic. Ind. 58, 191–197 (1993)
R.C. Pullar, C. Lai, F. Azough, Novel microwave dielectric LTCCs based upon V2O5 doped M2+Cu2Nb2O8 compounds (M2+ = Zn, Co, Ni, Mg and Ca). J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 1943–1946 (2006)
J.S. Kim, J.C. Lee, C.I. Cheon, H.J. Kang, Crystal structure and low temperature cofiring ceramic property of (1-x)(Li, Re)W2O8-xBaWO4 ceramics (Re = Y, Yb). Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45, 7397–7400 (2006)
H.F. Zhou, X.B. Liu, X.L. Chen et al., ZnLi2/3Ti4/3O4: a new low loss spinel microwave dielectric ceramic. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 261–265 (2012)
D. Zhou, C.A. Randall, L.X. Pang, Microwave dielectric properties of Li2WO4 ceramic with ultra-low sintering temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 348–350 (2011)
K. Fukuda, R. Kitoh, I. Awai, Microwave characteristics of TiO2BiO3 dielectric resonator. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 4584–4588 (1993)
C.F. Tseng, P.S. Tsai, Microwave dielectric properties of (1-x)ZnAl2O4-xCaTiO3 compound ceramic with controlled temperature coefficient. Ceram. Int. 39, 75–79 (2013)
D. Zhou, W.G. Qu, C.A. Randall, Ferroelastic phase transition compositional dependence for solid-solution [(Li0.5Bi0.5) x Bi1–x][Mo x V1–x]O4 scheelite-structured microwave dielectric ceramics. Acta. Mater. 59, 1502–1509 (2011)
H.T. Chen, B. Tang, S. Duan et al., Microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of Ba3.75Nd9.5Ti18–z(Mg1/3Nb2/3) z O54 ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 1081–1087 (2015)
D.H. Kim, C. An, Y.S. Lee et al., Microwave dielectric properties of ZnO-RO2-TiO2-Nb2O5 (R = Sn, Zr, Ce) ceramic system. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 22, 569–571 (2003)
K.S. Kim, S. Kim, H.K. Yun, O.Y. Soon, J.G. Park, Sintering behavior and microwave dielectric properties of the Zr1–x(Zn1/3Nb2/3) x TiO4 system with zinc-borosilicate glass. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 9, 126–130 (2008)
F.S. Song, Y.M. Li, Z.X. Shen et al., Effect of TiO2 addition amount on structure and microwave dielectric properties of Zn0.8Mg0.2ZrNb2O8 ceramic. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 43, 1725–1730 (2015)
X.C. Liu, F. Gao, C.S. Tian, Synthesis, low-temperature sintering and the dielectric properties of the ZnO-(1-x)TiO2-xSnO2 (x = 0.04–0.2). Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 693–699 (2008)
A. Baumgarte, R. Blachnik, New M2+M4+Nb2O8 phases. J. Alloys Compd. 215, 117–120 (1994)
J. Andrade, M.E. Villafuerte-Castrejon, R. Valenzuela, A.R. West, Rutile solid solutions containing M+(Li), M2+(Zn, Mg), M3+(Al) and M5+(Nb, Ta, Sb) ions. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 5, 147–149 (1986)
S. Wu, J. Luo, Mg-substituted ZnNb2O6–TiO2 composite ceramics for RF/microwaves ceramic capacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 8126–8129 (2011)
H.P. Wang, Q.L. Zhang, H. Yang, Low-temperature firing and microwave dielectric properties of ZnO–Nb2O5–TiO2–SnO2 ceramics with CuO–V2O5, Mater. Res. Bull. 40, 1891–1898 (2005)
E.S. Kim, D.H. Kang, Relationships between crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of (Zn1/3B2/3 5+) x Ti1–xO2 (B5+ = Nb, Ta) ceramics. Ceram. Int. 34, 883–888 (2008)
S.J. Penn, N.M. Alford, A. Templeton et al., Effect of porosity and grain size on the microwave dielectric properties of sintered alumina. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 1885–1888 (1997)
L.X. Li, X. Ren, Q.W. Liao, Crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of Zn0.9Ti0.8–xSn x Nb2.2O8 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 38, 3985–3989 (2012)
R.G. Hoagland, S.M. Valone, Emission of dislocations from grain boundaries by grain boundary dissociation. Philos. Mag. 95, 112–131 (2015)
H.F. Zhou, X.H. Tan, J. Huang, Sintering behavior, phase structure and adjustable microwave dielectric properties of Li2O-MgO-nTiO2 ceramics (1 ≤ n ≤ 5). J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 6475–6480 (2017)
P. Ruan, P. Liu, B.C. Guo, F. Li, Z.F. Fu, Microwave dielectric properties of ZnO-Nb2O5-xTiO2 ceramics prepared by reaction-sintering process. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 4201–4205 (2016)
W. Lei, Z.Y. Zou, Z.H. Chen, B. Ullah, A. Zeb, Controllable τ f value of barium silicate microwave dielectric ceramics with different Ba/Si ratios. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101, 25–30 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11464009, 61761015 and 11664008), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (Nos. 2017GXNSFFA198011, 2015GXNSFDA139033 and 2017GXNSFDA198027) and Research Start-up Funds Doctor of Guilin University of Technology (No. GUTQDJJ2017133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Zhou, H., Tan, X. et al. Adjustable microwave dielectric properties of ZnO–TiO2–ZrO2–Nb2O5 composite ceramics via controlling the raw ZrO2 content and sintering temperature. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 12055–12060 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9311-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9311-x