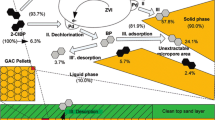
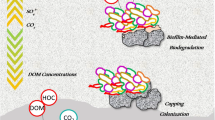
Abstract
The management and treatment of contaminated sediment is a worldwide problem and poses major technical and economic challenges. Nowadays, various attempts have been committed to investigating a cost-effective way in contaminated sediment restoration. Among the remediation options, in situ capping turns out to be a less expensive, less disruptive, and more durable approach. However, by using the low adsorption capacity materials, traditional caps do not always fulfill the reduction of risks that can be destructive for human health, ecosystem, and even natural resources. Active caps, therefore, are designed to employ active materials (activated carbon, apatite, zeolite, organoclay, etc.) to strengthen their adsorption and degradation capacity. The active capping technology promises to be a permanent and cost-efficient solution to contaminated sediments. This paper provides a review on the types of active materials and the ways of these active materials employed in recent active capping studies. Cap design considerations including site-specific conditions, diffusion/advection, erosive forces, and active material selection that should be noticed in an eligible remediation project are also presented.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Admassu W, Breese T (1999) Feasibility of using natural fishbone apatite as a substitute for hydroxyapatite in remediating aqueous heavy metals. J Hazard Mater 69:187–196. doi:10.1016/s0304-3894(99)00102-8
Alshawabkeh AN, Rahbar N, Sheahan T (2005) A model for contaminant mass flux in capped sediment under consolidation. J Contam Hydrol 78:147–165. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2005.05.003
Alther GR (1995) Organically modified clay removes oil from water. Waste Manag 15:623–628. doi:10.1016/0956-053X(96)00023-2
Apitz SE, Power EA (2002) From risk assessment to sediment management an international perspective. J Soils Sediments 2:61–66. doi:10.1007/BF02987872
Arega F, Hayter E (2008) Coupled consolidation and contaminant transport model for simulating migration of contaminants through the sediment and a cap. Appl Math Model 32:2413–2428. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2007.09.024
Asmala E, Saikku L, Vienonen S (2011) Import–export balance of nitrogen and phosphorus in food, fodder and fertilizers in the Baltic Sea drainage area. Sci Total Environ 409:4917–4922. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.08.030
Atkinson CA, Jolley DF, Simpson SL (2007) Effect of overlying water pH, dissolved oxygen, salinity and sediment disturbances on metal release and sequestration from metal contaminated marine sediments. Chemosphere 69:1428–1437. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.068
Azcue JM, Zeman AJ, Forstner U (1998a) International review of application of subaqueous capping techniques for remediation of contaminated sediments. Environmental Geotechnics, Vols 1–4. A a Balkema Publishers, Leiden
Azcue JM, Zeman AJ, Mudroch A, Rosa F, Patterson T (1998b) Assessment of sediment and porewater after one year of subaqueous capping of contaminated sediments in Hamilton Harbour, Canada. Water Sci Technol 37:323–329. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00214-5
Bailliez S, Nzihou A, Beche E, Flamant G (2004) Removal of lead (Pb) by hydroxyapatite sorbent. Process Saf Environ Prot 82:175–180. doi:10.1205/095758204322972816
Baker HM, Massadeh AM, Younes HA (2009) Natural Jordanian zeolite: removal of heavy metal ions from water samples using column and batch methods. Environ Monit Assess 157:319–330. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0537-6
Barth EF, Reible D, Bullard A (2008) Evaluation of the physical stability, groundwater seepage control, and faunal changes associated with an AquaBlok® sediment cap. Remediat J 18:63–70. doi:10.1002/rem.20183
Berg U, Neumann T, Donnert D, Nüesch R, Stüben D (2004) Sediment capping in eutrophic lakes–efficiency of undisturbed calcite barriers to immobilize phosphorus. Appl Geochem 19:1759–1771. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.05.004
Boyd SA, Lee J-F, Mortland MM (1988) Attenuating organic contaminant mobility by soil modification. Nature 333:345–347. doi:10.1038/333345a0
Bridges TS, Apitz SE, Evison L, Keckler K, Logan M, Nadeau S, Wenning RJ (2006) Risk-based decision making to manage contaminated sediments. Integr Environ Assess Manag 2:51–58. doi:10.1002/ieam.5630020110
Bridges TS et al. (2008) The four Rs of environmental dredging: resuspension, release, residual, and risk. Four Rs of Environmental Dredging Resuspension Release Residual & Risk
Calmano W, Hong J, Förstner U (1993) Binding and mobilization of heavy metals in contaminated sediments affected by pH and redox potential. Water Sci Technol 28:223–235. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.04.025
CETCO Corporation. Featured Case Studies: Sediment Remediation. http://www.cetco.com/en-us/Case-Studies/Environmental-Products/Sediment-Remediation. Accessed 9 May 2015
Cho Y-M, Smithenry DW, Ghosh U, Kennedy AJ, Millward RN, Bridges TS, Luthy RG (2007) Field methods for amending marine sediment with activated carbon and assessing treatment effectiveness. Mar Environ Res 64:541–555. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2007.04.006
Cho Y-M et al (2009) Field application of activated carbon amendment for in-situ stabilization of polychlorinated biphenyls in marine sediment. Environ Sci Technol 43:3815–3823. doi:10.1021/es802931c
Choi H, Agarwal S, Al-Abed SR (2008) Adsorption and simultaneous dechlorination of PCBs on GAC/Fe/Pd: mechanistic aspects and reactive capping barrier concept. Environ Sci Technol 43:488–493. doi:10.1021/es8015815
Corami A, Mignardi S, Ferrini V (2007) Copper and zinc decontamination from single- and binary-metal solutions using hydroxyapatite. J Hazard Mater 146:164–170. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.003
Cornelissen G et al (2011) Remediation of contaminated marine sediment using thin-layer capping with activated carbon–a field experiment in Trondheim Harbor, Norway. Environ Sci Technol 45:6110–6116. doi:10.1021/es2011397
Cornelissen G et al (2012) Large-scale field study on thin-layer capping of marine PCDD/F-contaminated sediments in Grenlandfjords, Norway: physicochemical effects. Environ Sci Technol 46:12030–12037. doi:10.1021/es302431u
Crane R, Scott T (2012) Nanoscale zero-valent iron: future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J Hazard Mater 211–212:112–125. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.073
del Rıo JG, Morando P, Cicerone D (2004) Natural materials for treatment of industrial effluents: comparative study of the retention of Cd, Zn and Co by calcite and hydroxyapatite Part I: batch experiments. J Environ Manag 71:169–177. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2004.02.004
Dixon KL, Knox AS (2012) Sequestration of metals in active cap materials: a laboratory and numerical evaluation. Remediat J 22:81–91. doi:10.1002/rem.21312
Eek E, Cornelissen G, Kibsgaard A, Breedveld GD (2008) Diffusion of PAH and PCB from contaminated sediments with and without mineral capping; measurement and modelling. Chemosphere 71:1629–1638. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.01.051
Eggen T, Majcherczyk A (2006) Effects of zero-valent iron (Fe0) and temperature on the transformation of DDT and its metabolites in lake sediment. Chemosphere 62:1116–1125. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.044
Eggleton J, Thomas KV (2004) A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environ Int 30:973–980. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.03.001
Elouear Z, Bouzid J, Boujelben N, Feki M, Jamoussi F, Montiel A (2008) Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions by activated phosphate rock. J Hazard Mater 156:412–420. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.036
El-Temsah YS, Joner EJ (2013) Effects of nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) on DDT degradation in soil and its toxicity to collembola and ostracods. Chemosphere 92:131–137. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.039
EPA. US (1998) Assessment and Remediation of Contaminated Sediments (ARCS) Program: Guidance for in-situ Subaqueous Capping of Contaminated Sediments. Assessment and Remediation of Contaminated Sediments Program, Great Lakes National Program Office, Chicago
Erdem E, Karapinar N, Donat R (2004) The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:309–314. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.028
Fox PJ, Lee J (2008) Model for consolidation-induced solute transport with nonlinear and nonequilibrium sorption. Int J Geomech 8:188–198. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1532-3641(2008)8:3(188)
Gheju M (2011) Hexavalent chromium reduction with zero-valent iron (ZVI) in aquatic systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 222:103–148. doi:10.1007/s11270-011-0812-y
Gibbs M, Özkundakci D (2011) Effects of a modified zeolite on P and N processes and fluxes across the lake sediment–water interface using core incubations. Hydrobiologia 661:21–35. doi:10.1007/s10750-009-0071-8
Gidley PT, Kwon S, Yakirevich A, Magar VS, Ghosh U (2012) Advection dominated transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in amended sediment caps. Environ Sci Technol 46:5032–5039. doi:10.1021/es202910c
Gilmour CC et al (2013) Activated carbon mitigates mercury and methylmercury bioavailability in contaminated sediments. Environ Sci Technol 47:13001–13010. doi:10.1021/es4021074
Go J, Lampert DJ, Stegemann JA, Reible DD (2009) Predicting contaminant fate and transport in sediment caps: mathematical modelling approaches. Appl Geochem 24:1347–1353. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.04.025
Graham M, Hartman E, He C, Droppo IG (2013) Examining thin layer cap behaviour in a freshwater industrial harbour. J Soils Sediments 13:1515–1526. doi:10.1007/s11368-013-0749-4
Hakstege A (2007) Description of the available technology for treatment and disposal of dredged material. Sediment Dredged Mater Treat 2:68–118. doi:10.1016/S1872-1990(07)80016-X
Hamidpour M, Kalbasi M, Afyuni M, Shariatmadari H, Holm PE, Hansen HCB (2010) Sorption hysteresis of Cd (II) and Pb (II) on natural zeolite and bentonite. J Hazard Mater 181:686–691. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.067
Hart B, Roberts S, James R, Taylor J, Donnert D, Furrer R (2003) Use of active barriers to reduce eutrophication problems in urban lakes. Water Sci Technol 47:157–163
Himmelheber DW, Pennell KD, Hughes JB (2011) Evaluation of a laboratory-scale bioreactive in situ sediment cap for the treatment of organic contaminants. Water Res 45:5365–5374. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.06.022
Huang H, Xiao X, Yan B, Yang L (2010) Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by using natural Chinese (Chende) zeolite as adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 175:247–252. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.156
Huang T, Zhou Z, Su J, Dong Y, Wang G (2013) Nitrogen reduction in a eutrophic river canal using bioactive multilayer capping (BMC) with biozeolite and sand. J Soils Sediments 13:1309–1317. doi:10.1007/s11368-013-0703-5
Hyötyläinen T, Karels A, Oikari A (2002) Assessment of bioavailability and effects of chemicals due to remediation actions with caging mussels (Anodonta anatina) at a creosote-contaminated lake sediment site. Water Res 36:4497–4504. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00156-2
Ichihara M, Nishio T (2013) Suppression of phosphorus release from sediments using water clarifier sludge as capping material. Environ Technol 34:2291–2299. doi:10.1080/09593330.2013.765924
Jacobs PH, Förstner U (1999) Concept of subaqueous capping of contaminated sediments with active barrier systems (ABS) using natural and modified zeolites. Water Res 33:2083–2087. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00432-1
Jamieson-Hanes JH, Lentz AM, Amos RT, Ptacek CJ, Blowes DW (2014) Examination of Cr (VI) treatment by zero-valent iron using in situ, real-time X-ray absorption spectroscopy and Cr isotope measurements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 142:299–313. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2014.07.031
Janssen EML, Beckingham BA (2013) Biological responses to activated carbon amendments in sediment remediation. Environ Sci Technol 47:7595–7607. doi:10.1021/es401142e
Jonker MT, Suijkerbuijk MP, Schmitt H, Sinnige TL (2009) Ecotoxicological effects of activated carbon addition to sediments. Environ Sci Technol 43:5959–5966. doi:10.1021/es900541p
Josefsson S, Schaanning M, Samuelsson GS, Gunnarsson JS, Olofsson I, Eek E, Wiberg K (2012) Capping efficiency of various carbonaceous and mineral materials for in situ remediation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran contaminated marine sediments: sediment-to-water fluxes and bioaccumulation in boxcosm tests. Environ Sci Technol 46:3343–3351. doi:10.1021/es203528v
Kanel SR, Manning B, Charlet L, Choi H (2005) Removal of arsenic (III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39:1291–1298. doi:10.1021/es048991u
Keum Y-S, Li QX (2004) Reduction of nitroaromatic pesticides with zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 54:255–263. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.08.003
Kim YS, Nyberg LM, Jenkinson B, Jafvert CT (2013) PAH concentration gradients and fluxes through sand cap test cells installed in situ over river sediments containing coal tar. Environ Sci Processes Impacts 15:1601–1612. doi:10.1039/C3EM00142C
Knox A, Kaplan D, Paller M (2006) Phosphate sources and their suitability for remediation of contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 357:271–279. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.07.014
Knox AS, Paller MH, Reible DD, Ma X, Petrisor IG (2008) Sequestering agents for active caps—remediation of metals and organics. Soil Sediment Contam 17:516–532. doi:10.1080/15320380802306610
Knox AS, Paller MH, Roberts J (2012) Active capping technology—new approaches for in situ remediation of contaminated sediments. Remediat J 22:93–117. doi:10.1002/rem.21313
Knox AS, Paller MH, Dixon KL (2014) Evaluation of Active Cap Materials for Metal Retention in Sediments. Remediat J 24:49–69. doi:10.1002/rem.21394
Kržišnik N, Mladenovič A, Škapin AS, Škrlep L, Ščančar J, Milačič R (2014) Nanoscale zero-valent iron for the removal of Zn2+, Zn (II)–EDTA and Zn (II)–citrate from aqueous solutions. Sci Total Environ 476:20–28. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.113
Lampert DJ, Sarchet WV, Reible DD (2011) Assessing the effectiveness of thin-layer sand caps for contaminated sediment management through passive sampling. Environ Sci Technol 45:8437–8443. doi:10.1021/es200406a
Lampert DJ, Lu X, Reible DD (2013) Long-term PAH monitoring results from the Anacostia River active capping demonstration using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) fibers. Environ Sci Processes Impacts 15:554–562. doi:10.1039/C3EM30826J
Larsson P (1985) Contaminated sediments of lakes and oceans act as sources of chlorinated hydrocarbons for release to water and atmosphere. Nature 317:347–349. doi:10.1038/317347a0
Lee J, Fox PJ (2009) Investigation of consolidation-induced solute transport. II: experimental and numerical results. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 135:1239–1253. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000048
Lee J, Fox PJ, Lenhart JJ (2009) Investigation of consolidation-induced solute transport. I: effect of consolidation on transport parameters. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 135:1228–1238. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000047
Lin J, Zhan Y, Zhu Z (2011) Evaluation of sediment capping with active barrier systems (ABS) using calcite/zeolite mixtures to simultaneously manage phosphorus and ammonium release. Sci Total Environ 409:638–646. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.10.031
Lin D, Cho Y-M, Werner D, Luthy RG (2014) Bioturbation delays attenuation of DDT by clean sediment cap but promotes sequestration by thin-layered activated carbon. Environ Sci Technol 48:1175–1183. doi:10.1021/es404108h
Liu C, Jay JA, Ford TE (2001a) Evaluation of environmental effects on metal transport from capped contaminated sediment under conditions of submarine groundwater discharge. Environ Sci Technol 35:4549–4555. doi:10.1021/es001763p
Liu C, Jay JA, Ika R, Shine JP, Ford TE (2001b) Capping efficiency for metal-contaminated marine sediment under conditions of submarine groundwater discharge. Environ Sci Technol 35:2334–2340. doi:10.1021/es0015702
Liu X, Wang M, Zhang S, Pan B (2013) Application potential of carbon nanotubes in water treatment: a review. J Environ Sci 25:1263–1280. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60161-2
Lowry GV, Murphy P, Marquette A, Reible D (2006) Sorbent-amended “active” sediment caps for in-place management of PCB-contaminated sediments. In: Contaminated soils, sediments and water. Springer, pp 379–391. doi:10.1007/0-387-28324-2_27
Ma X, Anand D, Zhang X, Tsige M, Talapatra S (2010) Carbon nanotube-textured sand for controlling bioavailability of contaminated sediments. Nano Res 3:412–422. doi:10.1007/s12274-010-1046-9
Machado S, Pinto S, Grosso J, Nouws H, Albergaria JT, Delerue-Matos C (2013a) Green production of zero-valent iron nanoparticles using tree leaf extracts. Sci Total Environ 445:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.033
Machado S et al (2013b) Application of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles to the remediation of soils contaminated with ibuprofen. Sci Total Environ 461–462:323–329. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.016
Mahabadi AA, Hajabbasi M, Khademi H, Kazemian H (2007) Soil cadmium stabilization using an Iranian natural zeolite. Geoderma 137:388–393. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.08.032
Martin Bouthot M-CW, Romeo Ciubotariu, Éric Blond (2004) Evaluation of the chemical compatibility of geosynthetics used as components of a subaqueous capping system for contaminated sediments. Paper presented at the 57th Canadian Geotechnical Conference, 5th Joint CGS/IAH-CNC Conference, Canada
Martin W et al (2008) The effect of organics on lead sorption onto Apatite II™. Appl Geochem 23:34–43. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.08.005
Martins M, Costa PM, Raimundo J, Vale C, Ferreira AM, Costa MH (2012) Impact of remobilized contaminants in Mytilus edulis during dredging operations in a harbour area: bioaccumulation and biomarker responses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 85:96–103. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.08.008
Masciangioli T, Zhang W-X (2003) Peer reviewed: environmental technologies at the nanoscale. Environ Sci Technol 37:102A–108A. doi:10.1021/es0323998
McDonough KM, Murphy P, Olsta J, Zhu Y, Reible D, Lowry GV (2007) Development and placement of a sorbent-amended thin layer sediment cap in the Anacostia River. Soil Sediment Contam Int J 16:313–322. doi:10.1080/15320380701285725
Mercier A, Wille G, Michel C, Harris-Hellal J, Amalric L, Morlay C, Battaglia-Brunet F (2013) Biofilm formation vs. PCB adsorption on granular activated carbon in PCB-contaminated aquatic sediment. J Soils Sediments 13:793–800. doi:10.1007/s11368-012-0647-1
Meric D, Rad MN, Barbuto S, Sheahan TC, Alshawabkeh AN, Shine J Testing the efficiency of a reactive core mat to remediate subaqueous, contaminated sediments. In: ASCE Proceedings of Geofrontiers 2011 Conference, 2011. doi:10.1061/41165(397)92
Meric D, Barbuto SM, Alshawabkeh AN, Shine JP, Sheahan TC (2012) Effect of reactive core mat application on bioavailability of hydrophobic organic compounds. Sci Total Environ 423:168–175. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.01.042
Meric D, Alshawabkeh AN, Shine JP, Sheahan TC (2014) Bioavailability of hydrophobic organic compounds in thin-layered capped sediments. Chemosphere 103:281–289. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.12.017
Millward RN, Bridges TS, Ghosh U, Zimmerman JR, Luthy RG (2005) Addition of activated carbon to sediments to reduce PCB bioaccumulation by a polychaete (Neanthes arenaceodentata) and an amphipod (Leptocheirus plumulosus). Environ Sci Technol 39:2880–2887. doi:10.1021/es048768x
Mumpton FA (1999) La roca magica: uses of natural zeolites in agriculture and industry. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:3463–3470
Murphy P, Marquette A, Reible D, Lowry GV (2006) Predicting the performance of activated carbon-, coke-, and soil-amended thin layer sediment caps. J Environ Eng 132:787–794. doi:10.1061/(asce)0733-9372(2006)132:7(787)
Näslund J, Samuelsson GS, Gunnarsson JS, Nascimento FJ, Nilsson H, Cornelissen G, Schaanning M (2012) Ecosystem effects of materials proposed for thin-layer capping of contaminated sediments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 449:27–39. doi:10.3354/meps09546
Nayar S, Goh B, Chou L (2004) Environmental impact of heavy metals from dredged and resuspended sediments on phytoplankton and bacteria assessed in in situ mesocosms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 59:349–369. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2003.08.015
Olsta J In-Situ Capping of Contaminated Sediments with Reactive Materials. In: Ports 2007@ s30 Years of Sharing Ideas: 1977–2007, 2007. ASCE, pp 1–9. doi:10.1061/40834(238)44
Oyanedel-Craver VA, Smith JA (2006) Effect of quaternary ammonium cation loading and pH on heavy metal sorption to Ca bentonite and two organobentonites. J Hazard Mater 137:1102–1114. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.03.051
Özkundakci D, Duggan IC, Hamilton DP (2011) Does sediment capping have post-application effects on zooplankton and phytoplankton? Hydrobiologia 661:55–64. doi:10.1007/s10750-009-9938-y
Palermo MR (1998) Design considerations for < i > in-situ</i > capping of contaminated sediments. Water Sci Technol 37:315–321. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00213-3
Palermo MR, Hinchee RE, Porta A, Pellei M (2005) A state-of-the-art overview of contaminated sediment remediation in the United States. In: Remediation and beneficial reuse of contaminated sediments. Proceedings of the First International Conference on Remediation of Contaminated Sediments, Venice, Italy
Paller MH, Knox AS (2010) Amendments for the in situ remediation of contaminated sediments: Evaluation of potential environmental impacts. Sci Total Environ 408:4894–4900. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.06.055
Park YJ, Ko JJ, Kim YI, Yun SL, Kim SJ, Lee BC Application of gypsum granule as a capping material to reduce phosphorus release from sediment of lake paldang. In: Materials science forum, 2007. Trans Tech Publ, pp 521–524. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.544-545.521
Park Y, Ayoko GA, Frost RL (2011) Application of organoclays for the adsorption of recalcitrant organic molecules from aqueous media. J Colloid Interface Sci 354:292–305. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2010.09.068
Peld M, Tõnsuaadu K, Bender V (2004) Sorption and desorption of Cd2+ and Zn2+ ions in apatite-aqueous systems. Environ Sci Technol 38:5626–5631. doi:10.1021/es049831l
Petersen EJ, Pinto RA, Shi X, Huang Q (2012) Impact of size and sorption on degradation of trichloroethylene and polychlorinated biphenyls by nano-scale zerovalent iron. J Hazard Mater 243:73–79. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.09.070
Qiao Q, Hua X, Dong D, Li T, Liang D, Li Y Effects of Tubificid bioturbation on realease of Cd and Zn from capping sediments. In: Water Resource and Environmental Protection (ISWREP), 2011 International Symposium on, 2011. IEEE, pp 2033–2036. doi:10.1109/ISWREP.2011.5893660
Randall PM, Yates BJ, Lal V, Darlington R, Fimmen R (2013) In-situ subaqueous capping of mercury-contaminated sediments in a fresh-water aquatic system, Part II-evaluation of sorption materials. Environ Res 125:41–51. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2013.03.010
Reible D, Hayes D, Lue-Hing C, Patterson J, Bhowmik N, Johnson M, Teal J (2003) Comparison of the long-term risks of removal and in situ management of contaminated sediments in the Fox River. Soil Sediment Contam 12:325–344. doi:10.1080/713610975
Reible D, Lampert D, Constant D, Mutch RD Jr, Zhu Y (2006) Active capping demonstration in the Anacostia River, Washington, DC. Remediat J 17:39–53. doi:10.1002/rem.20111
Riedel G, Sanders J, Osman R (1999) Biogeochemical control on the flux of trace elements from estuarine sediments: effects of seasonal and short-term hypoxia. Mar Environ Res 47:349–372. doi:10.1016/S0141-1136(98)00125-1
Roberts DA (2012) Causes and ecological effects of resuspended contaminated sediments (RCS) in marine environments. Environ Int 40:230–243. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2011.11.013
Rosen G, Leather J, Kan J, Arias-Thode YM (2011) Ecotoxicological response of marine organisms to inorganic and organic sediment amendments in laboratory exposures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1921–1930. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.06.023
Salonen V-P, Varjo E (2000) Gypsum treatment as a restoration method for sediments of eutrophied lakes–experiments from southern Finland. Environ Geol 39:353–359. doi:10.1007/s002540050014
Sarkar B, Xi Y, Megharaj M, Krishnamurti GS, Rajarathnam D, Naidu R (2010) Remediation of hexavalent chromium through adsorption by bentonite based Arquad® 2HT-75 organoclays. J Hazard Mater 183:87–97. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.06.110
Sarkar B, Naidu R, Rahman MM, Megharaj M, Xi Y (2012) Organoclays reduce arsenic bioavailability and bioaccessibility in contaminated soils. J Soils Sediments 12:704–712. doi:10.1007/s11368-012-0487-z
Sarkar B, Megharaj M, Shanmuganathan D, Naidu R (2013a) Toxicity of organoclays to microbial processes and earthworm survival in soils. J Hazard Mater 261:793–800. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.11.061
Sarkar B, Naidu R, Megharaj M (2013b) Simultaneous adsorption of tri-and hexavalent chromium by organoclay mixtures. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1–10. doi:10.1007/s11270-013-1704-0
Schmuhl R, Krieg H, Keizer K (2001) Adsorption of Cu (II) and Cr (VI) ions by chitosan: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Water SA 27:1–8
Seaman JC, Arey JS, Bertsch PM (2001) Immobilization of nickel and other metals in contaminated sediments by hydroxyapatite addition. J Environ Qual 30:460–469. doi:10.2134/jeq2001.302460x
Simpson SL, Apte SC, Batley GE (1998) Effect of short-term resuspension events on trace metal speciation in polluted anoxic sediments. Environ Sci Technol 32:620–625. doi:10.1021/es970568g
Simpson SL, Pryor ID, Mewburn BR, Batley GE, Jolley D (2002) Considerations for capping metal-contaminated sediments in dynamic estuarine environments. Environ Sci Technol 36:3772–3778. doi:10.1021/es025632v
Singh S, Ma L, Harris W (2001) Heavy metal interactions with phosphatic clay: sorption and desorption behavior. J Environ Qual 30:1961–1968
Singh R, Singh S, Parihar P, Singh VP, Prasad SM (2015) Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:247–270. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.10.009
Smith JA, Jaffe PR, Chiou CT (1990) Effect of ten quaternary ammonium cations on tetrachloromethane sorption to clay from water. Environ Sci Technol 24:1167–1172. doi:10.1021/es00078a003
Smith AM, Kirisits MJ, Reible DD (2012) Assessment of potential anaerobic biotransformation of organic pollutants in sediment caps. New Biotechnol 30:80–87. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2012.06.003
Sun X, Ghosh U (2007) PCB bioavailability control in Lumbriculus variegatus through different modes of activated carbon addition to sediments. Environ Sci Technol 41:4774–4780. doi:10.1021/es062934e
Sun H, Wang L, Zhang R, Sui J, Xu G (2006) Treatment of groundwater polluted by arsenic compounds by zero valent iron. J Hazard Mater 129:297–303. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.026
Sun H, Xu X, Gao G, Zhang Z, Yin P (2010) A novel integrated active capping technique for the remediation of nitrobenzene-contaminated sediment. J Hazard Mater 182:184–190. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.06.013
Tensar International Corporation. TRITON Case Study T17: Collins Cove Sedimen Cap, Beverly, Massachusetts. http://www.tensarcorp.com/FileDownload.ashx?id=%7b10326C67-FAA2-4E76-947F-7EE59B257767%7d. Accessed 23 May 2015
Tica D, Udovic M, Lestan D (2011) Immobilization of potentially toxic metals using different soil amendments. Chemosphere 85:577–583. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.085
Tomaszewski JE, Werner D, Luthy RG (2007) Activated carbon amendment as a treatment for residual DDT in sediment from a superfund site in San Francisco Bay, Richmond, California, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:2143–2150. doi:10.1897/07-179R.1
Valiela I, Costa J, Foreman K, Teal JM, Howes B, Aubrey D (1990) Transport of groundwater-borne nutrients from watersheds and their effects on coastal waters. Biogeochemistry 10:177–197. doi:10.1007/BF00003143
Viana P, Yin K, Zhao X, Rockne K (2007) Active sediment capping for pollutant mixtures: control of biogenic gas production under highly intermittent flows. Land Contamination Reclamation 15:413. doi:10.2462/09670513.879
Viana PZ, Yin K, Rockne KJ (2008) Modeling active capping efficacy. 1. Metal and organometal contaminated sediment remediation. Environ Sci Technol 42:8922–8929. doi:10.1021/es800942t
Wang Q, Li Y, Wang C, Wu Y, Wang P (2014) Development of a novel multi-functional active membrane capping barrier for the remediation of nitrobenzene-contaminated sediment. J Hazard Mater 276:415–421. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.063
Werner D, Higgins CP, Luthy RG (2005) The sequestration of PCBs in Lake Hartwell sediment with activated carbon. Water Res 39:2105–2113. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.03.019
Wingenfelder U, Hansen C, Furrer G, Schulin R (2005) Removal of heavy metals from mine waters by natural zeolites. Environ Sci Technol 39:4606–4613. doi:10.1021/es048482s
Xi Y, Mallavarapu M, Naidu R (2010) Preparation, characterization of surfactants modified clay minerals and nitrate adsorption. Appl Clay Sci 48:92–96. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2009.11.047
Xu Y, Schwartz FW, Traina SJ (1994) Sorption of Zn2+ and Cd2+ on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Environ Sci Technol 28:1472–1480. doi:10.1021/es00057a015
Yang S-C, Lei M, Chen T-B, Li X-Y, Liang Q, Ma C (2010) Application of zerovalent iron (Fe0) to enhance degradation of HCHs and DDX in soil from a former organochlorine pesticides manufacturing plant. Chemosphere 79:727–732. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.02.046
Yen TF (2001) In-situ stabilization of subsurface contaminants using microbial polymers. Proceedings, Industry Partnerships for Environmental Science and Technology DOE-NETL, Morgantown, WV
Yin H, Kong M (2015) Reduction of sediment internal P-loading from eutrophic lakes using thermally modified calcium-rich attapulgite-based thin-layer cap. J Environ Manag 151:178–185. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.01.003
Yin K, Viana P, Zhao X, Rockne K A Monte Carlo simulation approach for active caps in mixed contaminant environments. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Remediation of Contaminated Sediments, 2007
Yuan Q, Valsaraj KT, Reible DD, Willson CS (2007) A laboratory study of sediment and contaminant release during gas ebullition. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 57:1103–1111. doi:10.3155/1047-3289.57.9.1103
Yuan Q, Valsaraj KT, Reible DD (2009) A model for contaminant and sediment transport via gas ebullition through a sediment cap. Environ Eng Sci 26:1381–1391. doi:10.1089/ees.2008.0269
Yun SL, Kim SJ, Park YJ, Kang SW, Kwak PJ, Ko JJ, Ahn JH Evaluation of capping materials for the stabilization of contaminated sediments. In: Materials science forum, 2007. Trans Tech Publ, pp 565–568. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.544-545.565
Zamparas M, Deligiannakis Y, Zacharias I (2013) Phosphate adsorption from natural waters and evaluation of sediment capping using modified clays. Desalin Water Treat 51:2895–2902. doi:10.1080/19443994.2012.748139
Zeller C, Cushing B (2006) Panel discussion: remedy effectiveness: what works, what doesn’t? Integr Environ Assess Manag 2:75–79. doi:10.1002/ieam.5630020113
Zeman AJ (1994) Subaqueous capping of very soft contaminated sediments. Can Geotech J 31:570–577. doi:10.1139/t94-066
Zhao X, Viana P, Rockne K, Hey D, Schuh J, Lanyon R Combined active capping/wetland demonstration in the Chicago River. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Remediation of Contaminated Sediments, 2007
Zhu T, Fu D, Jafvert CT, Singh RP (2015) Modeling of gas generation from the river adjacent to the manufactured gas plant. RSC Adv 5:9565–9573. doi:10.1039/C4RA06627H
Zimmerman JR, Ghosh U, Millward RN, Bridges TS, Luthy RG (2004) Addition of carbon sorbents to reduce PCB and PAH bioavailability in marine sediments: Physicochemical tests. Environ Sci Technol 38:5458–5464. doi:10.1021/es048209q
Zimmerman JR, Werner D, Ghosh U, Millward RN, Bridges TS, Luthy RG (2005) Effects of dose and particle size on activated carbon treatment to sequester polychlorinated biphenyls and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1594–1601. doi:10.1897/04-368R.1
Acknowledgments
The project is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51179068, 51039001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Zhu, My., Zeng, Gm. et al. Active capping technology: a new environmental remediation of contaminated sediment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 4370–4386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6076-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6076-8