Abstract
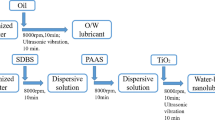
For environmental protection, energy conservation, and other reasons, water-based lubricants are increasingly chosen to replace oil lubricants. Water-based lubricants are divided into emulsified and solution types. Solution type water-based lubricants have attracted significant attention for the good stability, easy biodegradability, and safety for workers. However, some problems exist with current solution type water-based lubricants, such as poor lubricity and corrosion resistance. During the cold-rolling process, Al plate rolled using oil-based lubricant lubrication shows metallic luster, but that rolled using water-based lubricant shows corrosion spots, black strips, and no metallic luster. Therefore, this study mainly analyzed the reasons for the darkness of Al plate cold-rolled with water solution lubricants. The differences in plate surfaces lubricated by water solution and oil were investigated by scanning electron microscopy, auger electron spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The analysis results showed that the surface of the oil-lubricated sample is smooth, the oxygen content is low, and the oxide layer is thin, while the surface of the water solution-lubricated sample is rough, the oxygen content is high, the chemical composition is more complex, and the oxide layer is not uniform and thick.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guan Y S, Shi Q B, Zhang A H, et al. Study on lubrication effect of compound additive for rolling oil of aluminum plate (in Chinese). J Qinghai U, 2008, 26: 47–51
Sun J L. Rolling Process Lubrication Principle, Technology and Application. 2nd Ed. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2010
Zhang Z P. Tribological application and research of a new type of lubricant in aluminum foil rolling. Dissertation of Masteral Degree. Changsha: Central South University, 2005
Wang W X. Researches and development of lubricating in cold-rolled aluminum with water-based emulsion (in Chinese). J Shanghai Sec Polytechnic U, 2012, 29: 203–207
Wang H. Lubricants and Coolants in Metal Processing. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008. 95
Ma L R. Research on the lubricating characteristics and mechanisms of aqueous emulsions. Dissertation of Doctoral Degree. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2010. 10–12
Song S Y, Jiang W, Cheng C Y, et al. The properties of emulsion for cold rolling aluminum. Lubricat Oil, 2003, 05: 84–86
Liu L Z. Research status and development tendency of water solubility lubrication additive. Coal Sci Techno, 2011, 39: 122–124
Luo C H. Lubrication and surface quality in aluminum rolling. Lubricat Oil, 1995, 01: 42–49
Tu T T. Research on tribological performance of environmentally friendly water-based lubricants. Dissertation of Masteral Degree. Qingdao: Qingdao Techmology University, 2014. 27–30
Gong F X, Gou L Q, Qian Y N. Status and development of watersoluble lubricating additives. Synth Lubr, 2005, 32: 29–33
Kravchenko O V, Semenenko K N, Bulychev B M, et al. Activation of aluminum metal and its reaction with water. J Alloys Compd, 2005, 397: 58–62
Mao Y F, Shi Z M, Zhang B R, et al. Comparative test of aluminum corrosion behavior under different passivation layers. Microelectron Comput, 1986, 6: 19–22
Louaisil K, Dubar M, Deltombe R, et al. Simulation of interface temperature and control of lubrication in the study of friction and wear in cold rolling. Int J Mater Form, 2008, 1: 1239–1242
Chen Q, Wang X, Wang Z, et al. Preparation of water-soluble nanographite and its application in water-based cutting fluid. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2013, 8: 52
Fan M, Xu F, Sun L. Studies on hydrogen generation characteristics of hydrolysis of the ball milling Al-based materials in pure water. Int J Hydrogen Energ, 2007, 32: 2809–2815
Teng H T, Lee T Y, Chen Y K, et al. Effect of Al(OH)3 on the hydrogen generation of aluminum-water system. J Power Sources, 2012, 219: 16–21
Deng Z Y, Liu Y F, Tanaka Y, et al. Temperature effect on hydrogen generation by the reaction of γ-Al2O3-modified al powder with distilled water. J Am Ceramic Soc, 2005, 88: 2975–2977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Zhang, C., Wang, Y. et al. Analysis of surface and sub-surface of cold-rolled Al plate lubricated with water- or oil-based lubricants. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 60, 1407–1414 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-017-9075-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-017-9075-2