Abstract
Objective
To explore the anti-nociceptive effect of patchouli alcohol (PA), the essential oil isolated from Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Bent, and determine the mechanism in molecular levels.
Methods
The acetic acid-induced writhing test and formalin-induced plantar injection test in mice were employed to confirm the effect in vivo. Intracellular calcium ion was imaged to verify PA on mu-opioid receptor (MOR). Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) and MOR of mouse brain were expressed for determination of PA’s target. Cellular experiments were carried out to find out COX2 and MOR expression induced by PA.
Results
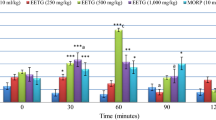
PA significantly reduced latency period of visceral pain and writhing induced by acetic acid saline solution (P<0.01) and allodynia after intra-plantar formalin (P<0.01) in mice. PA also up-regulated COX2 mRNA and protein (P<0.05) with a down-regulation of MOR (P<0.05) both in in vivo and in vitro experiments, which devote to the analgesic effect of PA. A decrease in the intracellular calcium level (P<0.05) induced by PA may play an important role in its anti-nociceptive effect. PA showed the characters of enhancing the MOR expression and reducing the intracellular calcium ion similar to opioid effect.
Conclusions
Both COX2 and MOR are involved in the mechanism of PA’s anti-nociceptive effect, and the up-regulation of the receptor expression and the inhibition of intracellular calcium are a new perspective to PA’s effect on MOR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Zhou GX. Literatures of Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. J Chin Med Mater (Chin) 2015;38:1986–1989.
Chakrapani P, Venkatesh K, Chandra Sekhar Singh B, Arun Jyothi B, Kumar P, Amareshwari P, et al. Phytochemical, pharmacological importance of patchouli (Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth) an aromatic medicinal plant. Inter J Pharm Sci Rev Res 2013;21:7–15.
Xie J, Lin Z, Xian Y, Kong S, Lai Z, Ip S, et al. (-)-Patchouli alcohol protects against Helicobacter pylori urease-induced apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response in human gastric epithelial cells. Int Immunopharmacol 2016;35:43–52.
Zheng YF, Xie JH, Xu YF, Liang YZ, Mo ZZ, Jiang WW, et al. Gastroprotective effect and mechanism of patchouli alcohol against ethanol, indomethacin and stress-induced ulcer in rats. Chem Biol Interact 2014;222:27–36.
Jeong JB, Shin YK, Lee SH. Anti-inflammatory activity of patchouli alcohol in RAW264.7 and HT-29 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 2013;55:229–233.
Su Z, Liao J, Liu Y, Liang Y, Chen H, Chen X, et al. Protective effects of patchouli alcohol isolated from Pogostemon cablin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Exp Ther Med 2016;11:674–682.
Yu JL, Zhang XS, Xue X, Wang RM. Patchouli alcohol protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Sur Res 2015;194:537–543.
Li YP, Yuan SF, Cai GH, Wang H, Wang L, Yu L, et al. Patchouli alcohol dampens lipopolysaccharide induced mastitis in mice. Inflammation 2014;37:1757–1762.
Wu XL, Ju DH, Chen J, Yu B, Liu KL, He JX, et al. Immunologic mechanism of patchouli alcohol anti-H1N1 influenza virus may through regulation of the RLH signal pathway in vitro. Curr Microbiol 2013;67:431–436.
Kiyohara H, Ichino C, Kawamura Y, Nagai T, Sato N, Yamada H. Patchouli alcohol: in vitro direct anti-influenza virus sesquiterpene in Pogostemon cablin Benth. J Nat Med 2012;66:55–61.
Feng XX, Yu XT, Li WJ, Kong SZ, Liu YH, Zhang X, et al. Effects of topical application of patchouli alcohol on the UV-induced skin photoaging in mice. Eur J Pharm Sci 2014;63:113–123.
Jeong JB, Choi J, Lou Z, Jiang X, Lee SH. Patchouli alcohol, an essential oil of Pogostemon cablin, exhibits antitumorigenic activity in human colorectal cancer cells. Int Immunopharmacol 2013;16:184–190.
Sah SP, Mathela CS, Chopra K. Antidepressant effect of Valeriana wallichii patchouli alcohol chemotype in mice: behavioural and biochemical evidence. J Ethnopharmacol 2011;135:197–200.
Zhang RX, Zhang M, Li A, Pan L, Berman BM, Ren K, et al. DAMGO in the central amygdala alleviates the affective dimension of pain in a rat model of inflammatory hyperalgesia. Neuroscience 2013;252:359–366.
Naghizadeh B, Mansouri MT, Ghorbanzadeh B. Ellagic acid enhances the antinociceptive action of carbamazepine in the acetic acid writhing test with mice. Pharm Biol 2016;54:157–161.
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Zarpelon AC, Fattori V, Manchope MF, Mizokami SS, Casagrande R, et al. Naringenin reduces inflammatory pain in mice. Neuropharmacology 2016;105:508–519.
Nalepa I, Vetulani J, Borghi V, Kowalska M, Przewlocka B, Pavone F. Formalin hindpaw injection induces changes in the [3H]prazosin binding to α1-adrenoceptors in specific regions of the mouse brain and spinal cord. J Neural Transm 2005;112:1309–1319.
Li QJ, Wang Z, Yao YX, Jin SH, Qian MZ, Li NN, et al. Loss of ICA69 potentiates long-lasting hyperalgesia after subcutaneous formalin injection into the mouse hindpaw. Neurochem Res 2015;40:579–590.
Thorn DA, Qiu Y, Jia S, Zhang Y, Li JX. Antinociceptive effects of imidazoline I2 receptor agonists in the formalin test in rats. Behav Pharmacol 2016;27:377–383.
Attoff K, Kertika D, Lundqvist J, Oredsson S, Forsby A. Acrylamide affects proliferation and differentiation of the neural progenitor cell line C17.2 and the neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Toxicol In Vitro 2016;35:100–111.
Yan XJ, Chai YS, Yuan ZY, Lu X, Jiang JF, Lei F, et al. Brazilein on neuron inflammation involved into the inhibition of NOD2/TNFα signaling during cerebral ischemic conditions. Chin J Nat Med 2016;14:354–362.
Wang XP, Lei F, Du F, Chai YS, Jiang JF, Wang YG, et al. Protection of gastrointestinal mucosa from acute heavy alcohol consumption: the effect of berberine and its correlation with TLR2, 4/IL1β-TNFα signaling. PLoS ONE 2015;10:e0134044.
Feng Y, Wang B, Du F, Li H, Wang S, Hu C, et al. The involvement of PI3K-mediated and L-VGCC-gated transient Ca2+ influx in 17β-estradiol-mediated protection of retinal cells from H2O2-induced apoptosis with Ca2+ overload. PLoS ONE 2013;8:e77218.
Yuan ZY, Lu X, Lei F, Chai YS, Wang YG, Jiang JF, et al. TATA boxes in gene transcription and poly (A) tails in mRNA stability: new perspective on the effects of berberine. Sci Rep 2015;5:18326.
Chai YS, Yuan ZY, Lei F, Wang YG, H J, Du F, et al. Inhibition of retinoblastoma mRNA degradation through poly (A) involved in the neuroprotective effect of berberine against cerebral ischemia. PLoS ONE 2014;9:e90850.
Li YC, Xian YF, Ip SP, Su ZR, Su JY, He JJ, et al. Antiinflammatory activity of patchouli alcohol isolated from Pogostemonis Herba in animal models. Fitoterapia 2011;82:1295–1301.
He JJ, Chen HM, Li CW, Wu DW, Wu XL, Shi SJ, et al. Experimental study on antinociceptive and anti-allergy effects of patchouli oil. J Essent Oil Res 2013;25:488–496.
Obermajer N, Kalinski P. Key role of the positive feedback between PGE2 and COX2 in the biology of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. OncoImmunology 2012;1:762–764.
Derry S, Moore RA. Single dose oral aspirin for acute postoperative pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;4:CD002067.
Al-Hasani R, Bruchas MR. Molecular mechanisms of opioid receptor-dependent signaling and behavior. Anesthesiology 2011;115:1363–1381.
Adams DJ, Trequattrini C. Opioid receptor-mediated inhibition of omega-conotoxin GVIA-sensitive calcium channel currents in rat intracardiac neurons. J Neurophysiol 1998;79:753–762.
Rhim H, Miller RJ. Opioid receptors modulate diverse types of calcium channels in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat. J Neurosci 1994;14:7608–7615.
Rusin KI, Giovannucci DR, Stuenkel EL, Moises HC. Kappa-opioid receptor activation modulates Ca2+ currents and secretion in isolated neuroendocrine nerve terminals. J Neurosci 1997;17:6565–6574.
Zamponi GW, Snutch TP. Modulation of voltage-dependent calcium channels by G proteins. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1998;8:351–356.
Zamponi GW, Snutch TP. Modulating modulation: crosstalk between regulatory pathways of presynaptic calcium channels. Mol Interv 2002;2:476–478.
Stein C. Opioid receptors. Annu Rev Med 2016;67:433–451.
Thirkettle-Watts D. Impedance-based analysis of mu opioid receptor signaling and underlying mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Rep 2016;6:32–38.
Jan WC, Chen CH, Hsu K, Tsai PS, Huang CJ. L-type calcium channels and μ-opioid receptors are involved in mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of naloxone. J Surg Res 2011;167:e263–e272.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the colleagues in our laboratory for their kind help and discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81374006 and No. 81073092) and the Special Foundation for New Drug Innovation of Tsinghua University (No. 20142000077), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Wang, Xp., Yan, Xj. et al. Anti-nociceptive effect of patchouli alcohol: Involving attenuation of cyclooxygenase 2 and modulation of mu-opioid receptor. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 25, 454–461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2952-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2952-4