Abstract
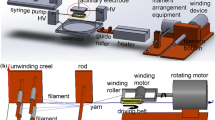
This study was focus on the influence of filament and roving location on yarn properties during embeddable and locatable spinning (ELS). ELS composite yarns were produced with various filament and roving locations on an experimental ring spinning frame. Besides yarn formation zone configurations, ELS yarn properties were compared including yarn hairiness, unevenness and tensile properties. Results showed that spinning triangles became larger; however, the reinforced composite spinning strand length kept constant. With a constant filament-roving spacing on each side of ELS, Filament spacing variations caused no significant changes of spun yarn hairiness, tenacities, imperfections and unevenness CV. For roving location variations with constant filament spacing, the reinforced strand length became longer as the roving spacing increased. Hairs exceeding 3 mm were lower for ELS yarn spun with 4 mm and 10 mm roving spacings than that spun with 6 mm, 8 mm and 12 mm roving spacings. Roving spacing variations had a trivial influence on ELS yarn unevenness; whereas, yarn tensile index variation coefficients fluctuated dramatically due to hairiness variations for different roving spacings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Xu, Z. Xia, X. Wang, J. Chen, W. Cui, W. Ye, C. Ding, and X. Wang, Text. Res. J., 81, 223 (2011).
C. I. Su, C. H. Liu, and J. Y. Jiang, Text. Res. J., 7, 815 (2003).
M. N. Sun and K. P. S. Cheng, Text. Res. J., 70, 261 (2000).
V. Subramaniam and K. S. Natarjan, Text. Res. J., 60, 234 (1990).
K. P. S. Cheng and M. N. Sun, Text. Res. J., 68, 520 (1998).
R. Nield and A. R. A. Ali, J. Text. Inst., 68, 223 (1977).
R. H. Yang, Y. Xue, and S. Y. Wang, Fibers Text. East. Eur., 18, 28 (2010).
W. Y. Liu, Y. P. Yu, J. H. He, and S. Y. Wang, Text. Res. J., 77, 200 (2007).
Z. Xia, X. Wang, W. Ye, H. A. Eltahir, and W. Xu, Text. Res. J., 82, 1255 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Xu, Q., Xia, Z. et al. An experimental study of influence of filament and roving location on yarn properties during embeddable and locatable spinning. Fibers Polym 13, 1196–1200 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-1196-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-1196-3