Abstract
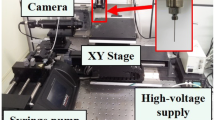
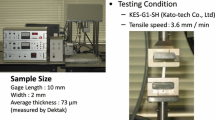
Wet electrospinning is a simple and efficient method to manufacture continuous nanofiber filaments. However, polyacrylonitrile nanofiber filaments collected using a static water bath are limited for application in certain areas due to their low degree of alignment and breaking stress values. To improve these properties, a novel countercurrent flowing liquid bath collector was combined with a multi-needle electrospinning device. The morphologies, crystalline structures, thermal behaviors and mechanical properties of filaments fabricated under different countercurrent bath liquid motion conditions were investigated. In addition, the forces acting on the nanofibers in the bundling triangular zone under countercurrent liquid bath motion were analyzed. The results showed that the average nanofiber diameter of the filaments decreased with an increase in bath solution motion forces. The maximum alignment degree and breaking stress of the nanofibers were 85 % and 0.63 cN/dtex, respectively, achieved using a liquid flow rate of 80 ml/min and water inlet diameter of 6 mm. The alignment degree of the assembled nanofibers in the bundling triangular zone could be increased by 57 % when using a countercurrent flowing liquid compared with a static liquid bath.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Wang, X. G. Wang, and T. Lin, J. Mater. Res., 27, 3013 (2012).
R. Dersch, T. Q. Liu, A. K. Schaper, A. Greiner, and J. H. Wendorff, J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem., 41, 545 (2003).
Y. Li, J. Zhang, C. Xu, and Y. F. Zhou, Science China-Chemistry, 59, 95 (2016).
A. Arinstein and E. Zussman, J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys., 49, 691 (2011).
F. L. Zhou, R. H. Gong, and I. Porat, J. Mater. Sci., 44, 5501 (2009).
F. L. Zhou, R. H. Gong, and I. Porat, Polym. Int., 58, 331 (2009).
H. T. Niu, W. M. Gao, T. Lin, X. G. Wang, and L. X. Kong, Polym. Eng. Sci., 54, 1495 (2014).
F. Ko, Y. Gogotsi, A. Ali, N. Naguib, H. H. Ye, G. L. Yang, C. Li, and P. Willis, Adv. Mater., 15, 1161 (2003).
J. H. Lee, D. W. Shin, K. B. Nam, Y. H. Gim, H. S. Ko, D. K. Seo, G. Hui lee, Y. H. Kim, S. W. Kim, T. S. Oh, and J. B. Yoo, Polymer, 84, 52 (2016).
L. Tian, J. Li, and Z. J. Pan, Adv. Mater. Res., 796, 306 (2013).
S. Ma, J. Liu, Q. Liu, J. Liang, Y. Zhao, and H. Fong, Mater. Des., 95, 387 (2016).
M. S. Khil, S. R. Bhattarai, H. Y. Kim, S. Z. Kim, and K. H. Lee, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 72B, 117 (2005).
Y. Liu, J. Li, and Z. J. Pan, J. Polym. Res., 18, 2055 (2011).
A. Varesano, F. Rombaldoni, G. Mazzuchetti, C. Tonin, and R. Comotto, Polym. Int., 59, 1606 (2010).
E. Smit, U. Buttner, and R. D. Sanderson, Polymer, 46, 2419 (2005).
L. Tian, C. Zhao, and Z. Pan, Sci. Adv. Mater., 7, 2327 (2015).
J. Liu, L. He, S. Ma, J. Liang, Y. Zhao, and H. Fong, Polymer, 61, 20 (2015).
J. S. Youm, J. H. Kim, C. H. Kim, J. C. Kim, Y. A. Kim, and K. S. Yang, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 133 (2016).
X. F. Wang, K. Zhang, M. F. Zhu, B. J. S. Hsiao, and B. J. Chu, Macromol. Rapid Commun., 29, 826 (2008).
C. Liu, Highpolymer Mater. Sci. Eng., 27, 94 (2011).
D.-N. Nguyen, Y. Hwang, and W. Moon, Eur. Polym. J., 77, 54 (2016).
W. E. Teo, R. Gopal, R. Ramaseshan, K. Fujihara, and S. Ramakrishna, Polymer, 48, 3400 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Yq., Zhang, X. & Pan, Zj. A Novel Method to Fabricate High Strength Nanofiber Filaments: Morphology, Crystalline Structure, and Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Fibers Polym 19, 1245–1254 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-018-8011-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-018-8011-8